Cybercrime is happening at record levels and the statistics are getting more alarming every year.
Cybercrime cost the world over $1 trillion in 2020, according to a report by Atlas
Packetlabs also compiled a list of cybersecurity statistics for 2020. Here are some highlights of the report:
- Reported cybercrimes in the USA increased by 300% since the start of the pandemic
- Over 80% of businesses in Canada were hit by phishing and 50% by malware in 2020
- In Q4 2020, 74% of scams used HTTPS sites to launch phishing attacks
- Between 2018 and 2020, the average cost of downtime caused by ransomware increased seven times from $4,800 to $283,000
- In 2020, the total ransom amount paid increased by 311% from 2019 reaching nearly $350 million, but only 8% of victims got their data back
What do all these figures have to do with website
What is a website security certificate?
A website
When you see an HTTPS or black padlock icon preceding the domain name on the URL, it means that the website is secured by a website
How a website security certificate works
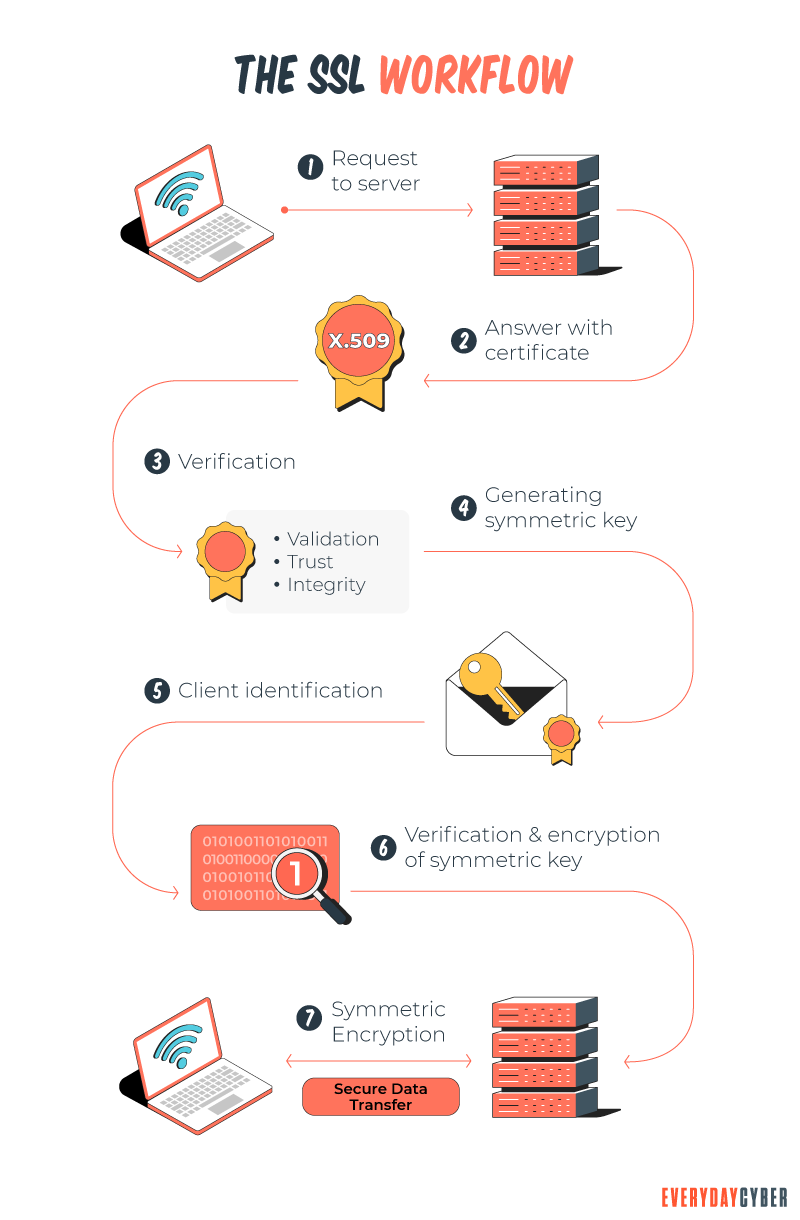
When you want to connect to a secured website, here are the steps that take place:
- Your browser asks the web server to identify itself
- The server sends a copy of the website
security certificate to the browser - The browser forwards a message to the server to confirm that the certificate is in order
- The server will, in turn, send an acknowledgment that’s digitally signed and start an encrypted communication with the browser
- Data can then be exchanged safely between your browser and the web server
Why a website security certificate is important
Whether you’re a general information or business website, a website
Google has made HTTPS an important factor in its search algorithm for ranking websites. Having it on your URL will give you a chance to be noticed by Google and potentially earn a higher ranking.
You’ll want to prove to people that you’re you, especially if you’re a business or organization. A website
Once you’ve asserted your
How HTTPS works
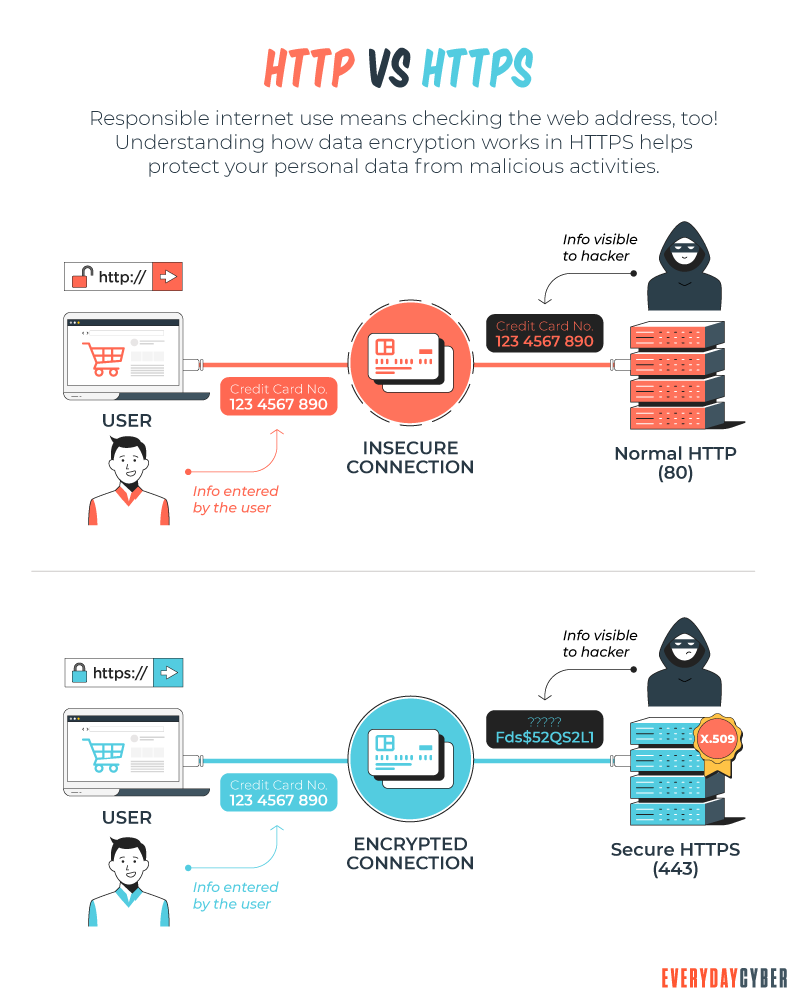
HTTPS is short for Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure. It is the secure version of HTTP. HTTP and HTTPS are communication protocols responsible for transmitting data between a web browser and a website.
Technically, HTTPS and HTTP work in the same way, except that HTTPS uses an encryption protocol to secure communications. The protocol is known as Transport Layer
The private key. This key is controlled and kept private by the owner of the website. It resides on a web server and is used to decrypt data encrypted by the public key.
The public key. This key is accessible to anyone who wants to transmit information in a secure way, meaning that the information should be encrypted. The encrypted information can only be decrypted by the private key.
When information is transmitted over standard HTTP, all communications travel as plain text. Unencrypted data is highly accessible to anyone who has the right skills and tools. It is also vulnerable to interception through on-path attacks while a web browser and server are communicating.
The handshake protocol
HTTPS always begins with an SSL handshake, an asymmetric cryptography process for establishing a secure communication channel for the server and the client. The handshake happens instantly and automatically if everything is in order.
A failed handshake results in the termination of the connection, usually followed by a warning message in the client’s browser.
source: https://www.makeuseof.com/tag/website-security-certificate-care/
What are the types of website security certificates
Website
By validation levels:
Here the are three types of website
1. Domain validation (DV) certificate
A DV certificate is validated against a domain registry to check ownership of the website domain. However, it’s not recommended for commercial websites because it does not offer organizational information. Website visitors cannot validate whether the website is legitimate or not. DV certificates can be used where authentication is not needed, such as protected internal systems.
2. Organization validation (OV) certificate
The certificate authority authenticates an organization against the domain registry and business registry databases hosted by governments. The CA may also look into organizational documents and interview personnel to gather legitimate business information. This is the ideal certificate for commercial and public-facing websites.
3. Extended validation (EV) certificate
An EV certificate offers the highest level of validation because it goes through additional validation steps. It includes details not found in DV and OV certificates. EV certificate is the global standard for encrypting data because it is extremely difficult to impersonate an EV-enabled website. The world’s leading organizations and businesses have adopted it to protect their brand and ensure user trust. They also use it for sensitive processes, such as area logins and front-facing webpages.
By functionalities
Website
1. Single domain SSL certificate
This is the simplest SSL certificate covering only one domain and excluding subdomains and other websites you own.
2. Multi-domain SSL certificate
A multi-domain certificate is also known as a unified communications (UCC) SSL certificate. It allows you to include up to 100 domains and subject alternative names (SANs), facilitating communication between servers and browsers at the same time.
3. Wildcard SSL certificate
A wildcard certificate allows you to use a single certificate for the domain and an unlimited number of subdomains. For example, a single certificate can be used for:
- everydaycyber.net
- blog.everydaycyber.net
- forum.everydaycyber.net
It’s a more affordable option than investing in a certificate for each domain and subdomain.
4. Multi-domain wildcard SSL certificate
This type of certificate allows big organizations to secure multiple domain names and subdomains, including subject alternative names, with a single certificate.
By entering your email address you agree to receive emails from EveryDayCyber. We'll respect your privacy and you can unsubscribe at any time.
What are the common SSL attacks and vulnerabilities?
The SSL/TLS protocol is widely used, making it a potential breeding ground for attacks. As with all technology, SSL has its own downside. The most common is improperly configured servers that can expose data instead of securing it.
Following are typical SSL attacks and vulnerabilities that cybercriminal can exploit:
1. Man-in-the-middle (MITM) attacks
To launch an MITM attack, cybercriminals impersonate a trusted website so they can gain the trust of the communicating parties and eavesdrop on secure conversations.
Attackers often exploit unsecured or inadequately protected wireless access points to gain entry. They can steal a website’s server key, allowing an attacker to appear as the server.
Attackers can also steal the root key of a compromised certificate authority (CA) and issue a fake certificate generated by the stolen key. With a fake certificate, attackers can then inject malware to redirect users to fake banking sites and phishing sites, for example.
2. Advanced persistent threat (APT)
With the use of malware, APT attackers steal SSL/TLS keys and certificates for use in communications fraud and data theft. Cybercriminals exploited the Heartbleed malware resulting in a data breach of more than 4.5 million patient records at the Community Health System (CHS). The criminals worked around the CHS firewall and took advantage of a vulnerable system behind the firewall.
3. SSL stripping attacks
An SSL stripping attack is a cyberattack in which hackers downgrade a web connection from the more secure HTTPS to the less secure HTTP. This reverts all communications into unencrypted form and paves the way for a man-in-the-middle intrusion.
At this point, the MITM attacker is in control. He sends the victim’s request to the genuine server and sends back the reply to the victim’s browser in HTTP. All communications are now in plain text format, allowing the attacker to gather all the data he wants.
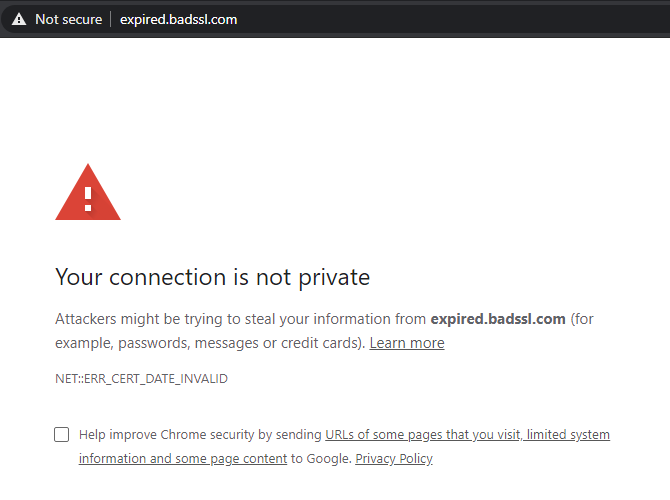
4. Expired SSL/TLS certificates
Expired certificates risk degrading encryption and authentication. This opens your website to attacks and viruses. You may also risk losing users if they see a warning message that says “Your connection is not private”. Your traffic could drop and you could lose business.
5. Self-signed wildcard certificates
Some server administrators resort to quick and easy ways of providing SSL certificates for websites. They create self-signed wildcard certificates using free, OpenSSL. These certificates are not signed by a publicly trusted certificate authority but by the administrator’s own private key.
This practice erodes trust because the certificate is not validated by a credible certificate authority. Websites with self-signed certificates show warning pages with error messages, such as:
- “error_self_signed_cert”
- “sec_error_untrusted_issuer”
- “err_cert_authority_invalid”
These messages drive visitors away and drastically affect traffic on your website. People hesitate to share their personal information, such as usernames, passwords, bank and credit card details and
Moreover, websites labeled as “not secure” are easy targets for cybercriminals to launch man-in-the-middle attacks. Once an MITM strike is happening and users bypass the
6. Fake certificate authorities
Fake, untrusted and unknown certificate authorities have joined cybercrime networks to fool unsuspecting victims. Internet
The fake certificates bear the common names of their target websites. Many of the fake certificates impersonate known brands, such as Facebook, GoDaddy, iTunes and YouTube. But because the certificates are not signed by trusted certificate authorities, they are regarded by mainstream browsers as invalid. For banks, the danger lies in online traffic originating from apps and non-browser software that may fail to check the validity of SSL certificates.
Fake certificates alone are not enough to carry out an attack. The attacker would need to set up rogue access points to establish contact to some system between the victim and the server. The attacker can then monitor traffic and direct it to the intended IP address under his control where he can steal credentials and other financial information.
7. Attacker-encrypted communications
Cybercriminals are using encryption to deliver malware undetected, eavesdrop on private conversations, disrupt secure transactions and extract data over encrypted communication channels. An increase in encrypted traffic will mean more attack vectors for criminals.
8. Phishing attacks
Vulnerable SSL certificates allow malicious actors to use social engineering to trick people to go to fraudulent sites under their control where they can capture financial and personal information.
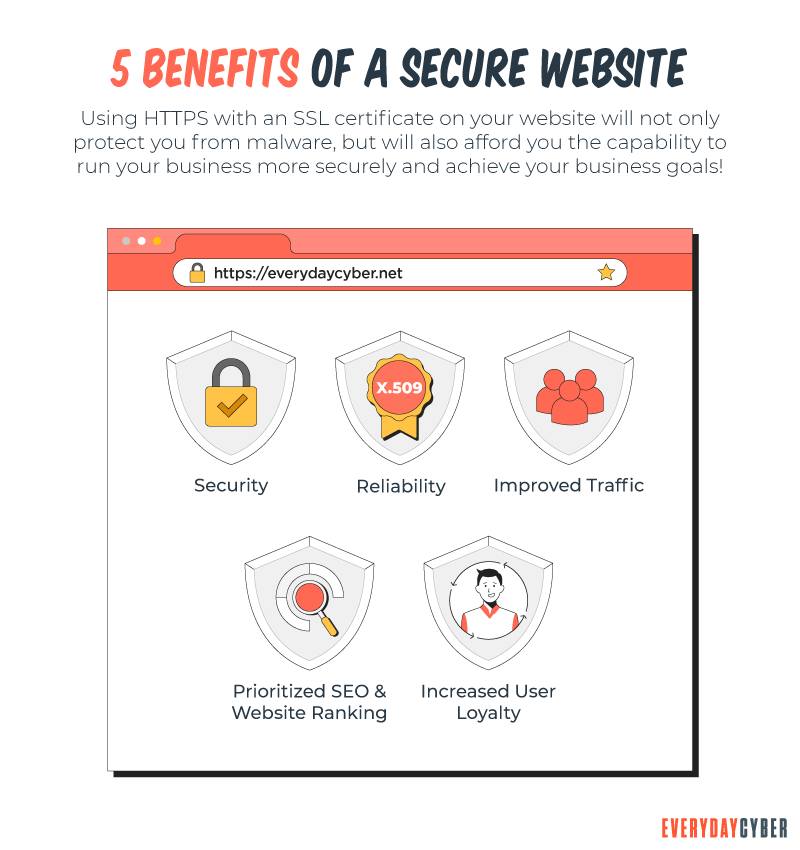
Benefits of a Website Security Certificate
Obtaining and implementing a website
They Protect Data
The core objective of
They Affirm Your Identity
The second most important role of a
Website spoofing is a cyber crime mainstay. By protecting your website with a
Improved Search Engine Ranking
Google has literally made it mandatory to use HTTPS to have a chance of being returned in its top search results. You simply have no chance of having your website or any of its content displayed on the first page of search results if a
Helps You Satisfy PCI/DSS Requirements
If your website supports ecommerce or any form of online payments, you will likely know a thing or two about PCI/DSS requirements. To receive online payments, your website must be PCI compliant. Having a website
Improves Customer Trust
Beyond just encryption and authentication,
What should you do if you see a certificate warning?
Chances are you’ll come across a certificate alert while browsing the Internet. If you get an alert on a website you’re trying to access, click on the padlock to check the details. The certificate may be expired or is being used fraudulently, in which case you shouldn’t trust it.
If you see the certificate alert on a website you trust and have been accessing before, you can check the website’s social media feed where you can see updates on downtime,
How do you choose the right website security certificate?
It’s important to choose the right
As to functionality, a single domain certificate may be sufficient to secure your small business, but you may need a multi-domain wildcard SSL certificate for your multiple branches and locations.
As to validation, a DV certificate should be able to meet the requirements of your small business. However, if you’re a big commercial website or corporation that deals with high-risk data like health records or bank accounts, you’ll need an EV certificate to provide the highest level of validation and
Our final thoughts: Do you want people to find your ecommerce website? Do you want them to feel comfortable and safe doing business with you? Do you want your audience to keep coming back because they feel more secure? If your answer is yes to all the questions, then you need the right
Get a website security certificate!
By entering your email address you agree to receive emails from EveryDayCyber. We'll respect your privacy and you can unsubscribe at any time.
Recommended Reading
What is a Rogue Certificate?
A rogue certificate is a valid certificate issued by a legitimate certificate authority. However, it’s untrustworthy because either it was compromised or was issued to the wrong party.
What is DNS Hijacking?
DNS hijacking is no laughing matter. It is a serious security threat that is consuming the cyber world. The critical role of DNS for network security has made a primary target for facilitating mass data theft.
What is Typosquatting?
Cybercriminals target visitors that accidentally mistype website addresses directly into their browsers. They use typosquatting, also called URL hijacking, to deceive visitors and lead them to malicious sites they themselves have set up.
What is the Dark Web?
The dark web is the part of the world wide web that is hardest to reach because it lies at the center of the onion or the bottom portion of the proverbial submerged iceberg.
What is Adware?
Adware, known as advertising supported software, makes money by displaying ads - popups, inline, banner. ANNOYING!!, but typically used to support free software.
Things About Ryuk Ransomware You Need to Know Right Now
Ryuk ransomware is one of the most dreaded malware to date. It encrypts or steals corporate data to extort millions of dollars from its victims. The Covid-19 crisis greatly influenced the recent rise in ransomware. The remote work response to the pandemic created huge gaps in the worlds cyber defenses. Threat actors saw these vulnerabilities as opportunities to spread large-scale ransomware attacks.


