So, the first image that probably comes to mind when you hear the term worm, and in our case computer worm, is a squirmy invertebrate that you found on a sidewalk after a rainstorm or as a kid, you played in the dirt with or if you are into fishing (not phishing) you might have used them as bait. This is not the kind of worm we are talking about. Computer worms are nasty little creators created to do evil things.
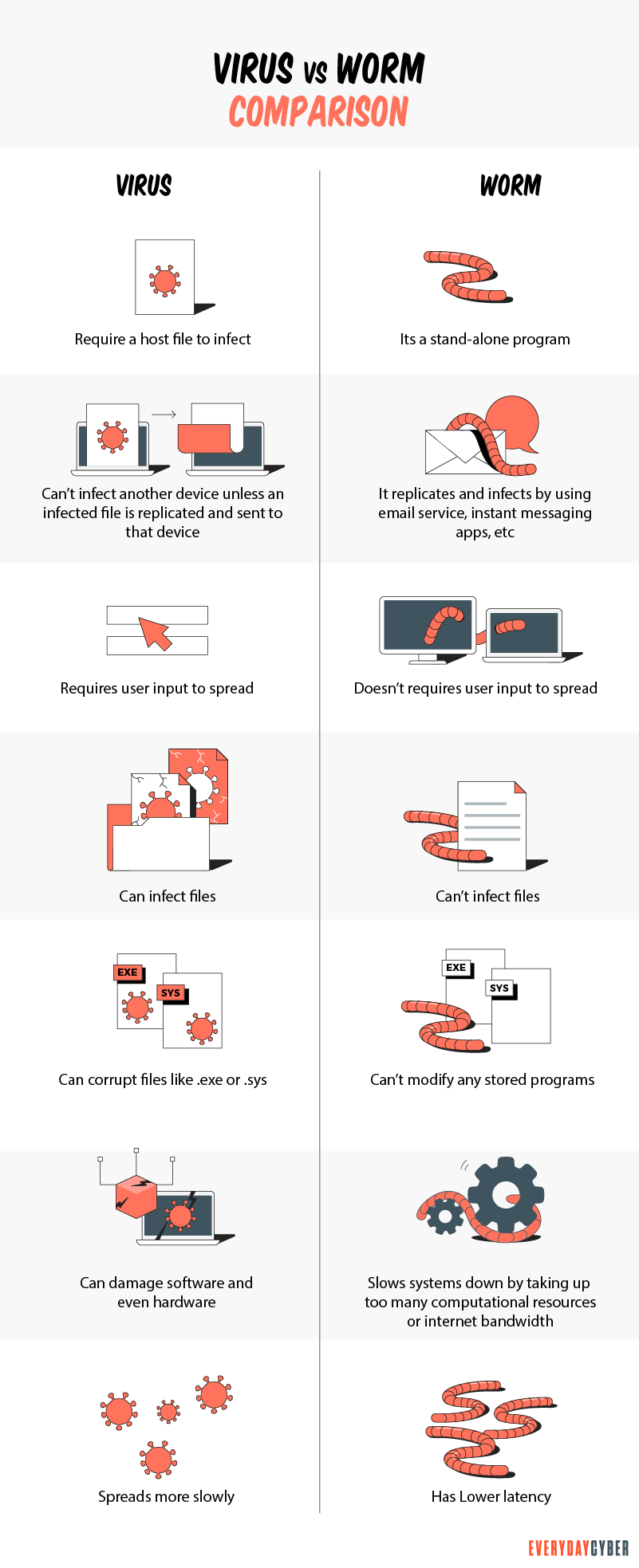
Computer worms are another form of malware (malicious software) that infects our devices like viruses, trojans, and spyware. Part of their mission may be to do exactly what those other types of malware do. But there is one specific characteristic that computer worms have that the others don’t, and that is the ability to self-replicate and send copies of themselves to other devices. Many cyber experts consider worms to be a subspecies of viruses. but unlike viruses, they can travel from device to device and across networks without any human action.
So how do computer worms work?
Computer worms are designed to exploit known
Once a worm is on your device, it can corrupt files, steal private information, modify system settings to make your device unusable or even install backdoors. Backdoors give cybercriminals access to your device, making it even more vulnerable.
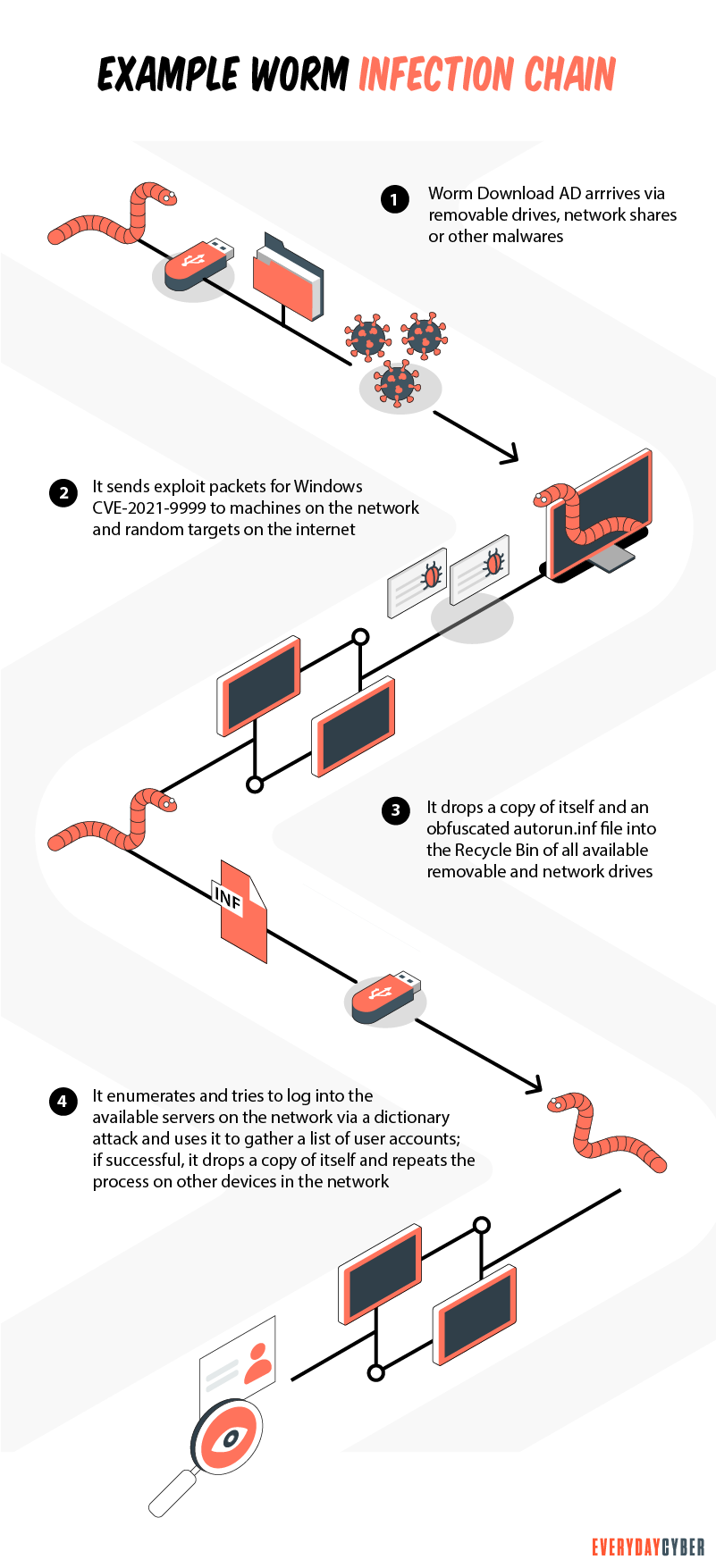
How do you know if a computer worm is on your device?
As with all malware, ultimately having a quality antivirus /
Paying attention to how your devices are behaving is a key strategy to recognizing the possibility you have a worm.
-
- Monitor the storage space on your device. Since worms replicate, they can start consuming free space on your device.
- Monitor your performance. Worms can consume processing power, so if your device is feeling sluggish, it could be a worm.
- Keep an eye out for missing files or even new files on your device. One of the more common behaviors of worms is to delete or replace files on the devices they infect.
If you fear that your machine is infected, immediately run a
By entering your email address you agree to receive emails from EveryDayCyber. We'll respect your privacy and you can unsubscribe at any time.
Recommended Reading
What is a certificate authority CA and what do they do?
Certificate authorities are the guardians of digital identity. They come in both public and private capacities. Certificates issued by them are trusted because information are validated from the requester’s own records and/or from third party sources.
What is the Dark Web?
The dark web is the part of the world wide web that is hardest to reach because it lies at the center of the onion or the bottom portion of the proverbial submerged iceberg.
What to do if your phone is lost or stolen
When your phone is lost or stolen, it is more than just a pricey handheld that is lost. Our phones keep track of our lives. If you’ve lost your phone, there are things you can do to track, locate, and recover it depending on the type of phone you have. Read this to get tips on how.
What is a Potentially Unwanted Program (PUP)?
PUPs refer to programs, applications and other software downloaded onto computers or mobile devices that may have an adverse impact on user privacy or security. The term “potentially unwanted program” was coined by McAfee to distinguish the program from malware.
What is Spear Phishing?
Spear phishing is a targeted cyberattack to steal your information. You should be aware of the dangers of this and how to address them.
What you should know about Chatbots And cybersecurity
Chatbots are conversational assistants that automate repetitive chores. We like them because they assist them in completing jobs swiftly and without the need for human interaction. But an unprotected chatbot can be a security problem. Hackers can use defenseless AI chatbots to carry out nefarious activities. Read to learn more.


