Did you know that 91% of successful data breaches started with a
But are you confident your network is secure enough to ward off any
Spear Phishing Definition
Spear phishing is a highly targeted form of phishing. It’s a more advanced kind of traditional phishing uses convincing language.
Before launching a
Signs of Spear Phishing Attacks
Spear phishing attacks are laced with social engineering techniques that make it difficult for targets to discover the red flags. But the warning signs of
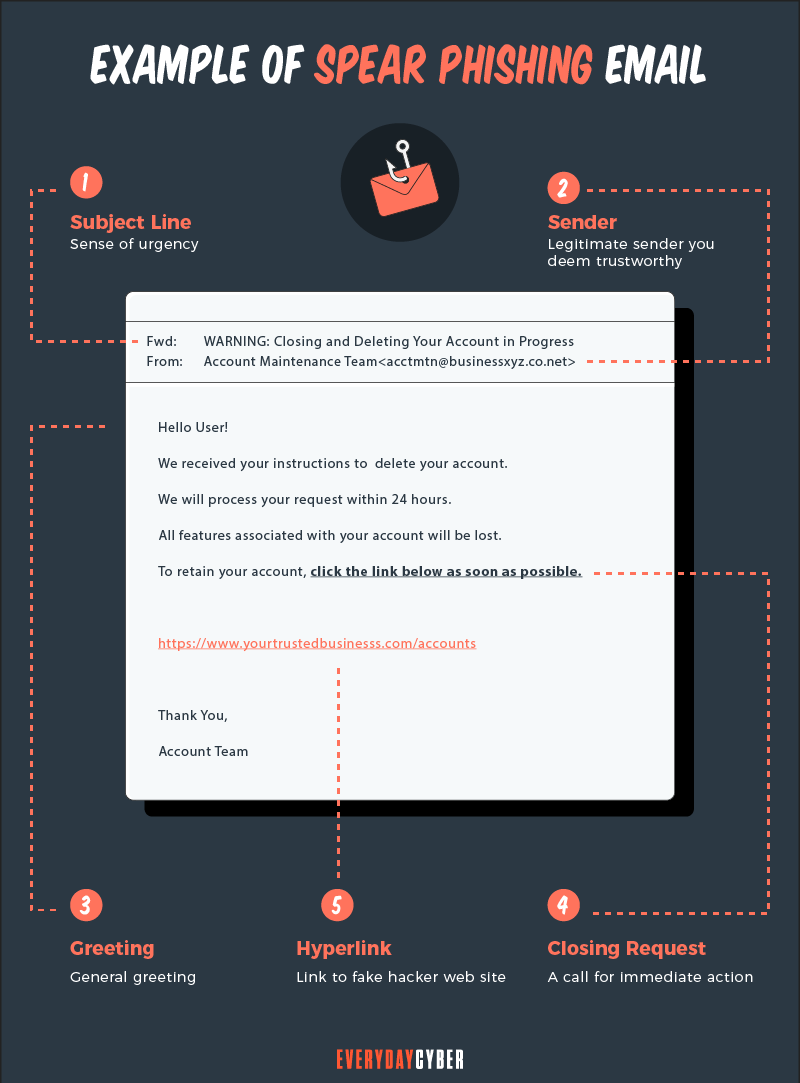
Spoofed address of the sender of spear phishing emails
It’s important to check if the sender’s email address matches those from earlier messages. Spear phishers frequently spoof or falsify the sender of a
Example: The sender of
To check: Hover your cursor over the alleged sender’s email address. If it doesn’t match the resulting email address when you hover your cursor, it’s a characteristic of a phishing attack.
Unusual requests and messages
In a
Example: Your manager sends an email asking you to provide him or her with a list of the names of department heads even though you’re not part of the human resources team. Or your “security team” emails you and requests you to download an updated software when this is often handled automatically.
To check: Find out whether the request is sensible and consistent with the business’ internal policies by calling the sender.

Strange language
One of the goals of
Example: An email from a financial executive of a company you know suddenly uses informal messaging, instead of the usual formal tone.
To check: Contact the sender through
Requests for urgent response
Subject lines for
Example: The subject line reads “Urgent Action Required” to scare you out of your wits and do what the sender is asking you to do.
To check: Don’t panic and don’t click on any link or download an attachment. Check the sender’s email address against previous emails to make sure they match. Look for other signs of a scam, such as the use of strange language or unusual salutation. Better yet, call the sender if he/or she really sent the email.
Suspicious timing
Spear phishing attacks can be detected by the email timestamps. Emails from friends sent during your working hours when they know you can’t respond to them are a warning sign. So are emails from coworkers sent outside of business hours.
Example: Your friend Jane sends you an email that needs urgent response during your office hours.
To check: Examine the timestamp of each
Questionable links and attachments
A
Example: An email message asks you to click on everydaycyber.com, a malicious site. The legitimate site is everydaycyber.net.
To check: Hover your cursor over any links in the message to see their URLs. Don’t click on it if it directs you to a malicious website. Check for subtle changes in the domain name and don’t click if there are any. Don’t open mysterious attachments either as they may contain malicious software. Inform your
By entering your email address you agree to receive emails from EveryDayCyber. We'll respect your privacy and you can unsubscribe at any time.
How Spear Phishing Attacks Work
Spear phishing works through the use of:
- Emails
- Social media
- Text messaging
- Phone calls often called voice-phishing or vishing
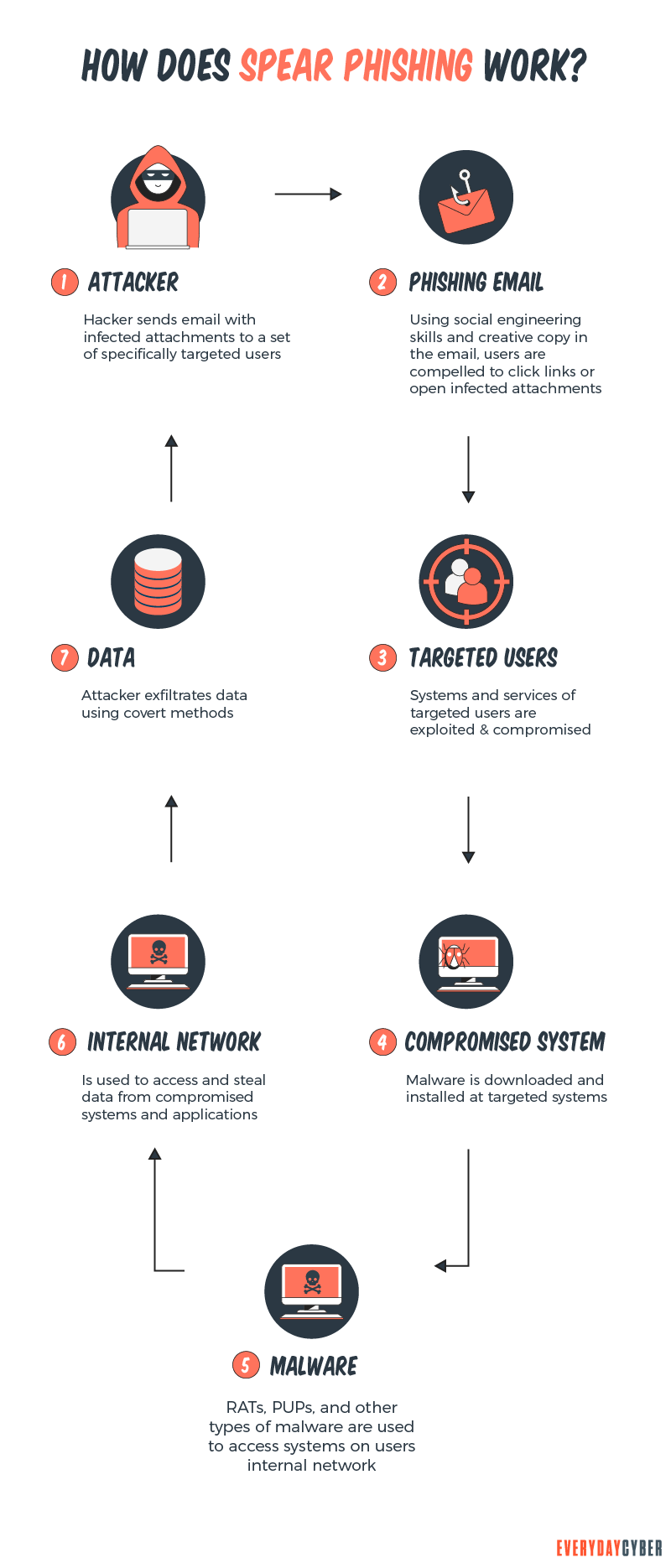
Spear phishers use various methods to gain access to the corporate network and collect private information. Here are the common ones:
Use social engineering tactics
Since
Spear phishing emails specifically target those who post personal information online. While browsing a social networking site, they might browse particular profiles. They can discover a person’s email address, friend list, current location, and any posts concerning recently acquired gadgets and technology.
With all of this knowledge, an attacker could pose as a friend or a familiar figure. He or she then sends targeted phishing attacks with a message that seems genuine but is actually fake.
Identify their targets and their email addresses
In
They can obtain an organization’s email addresses in a number of ways. Cybercriminals’ preferred method is using scripts to get email addresses from the major search engines.
You’d be shocked at how many emails can be obtained in this manner. You’d also be surprised at how huge an organization’s
Send the emails
Once the spear phishers get the email addresses of the select few persons they are aiming for, they start sending personalized emails. If the recipients haven’t had thorough
Spear phishing emails frequently include urgent justifications for why they require sensitive data. They entice their victims to click on a link that leads to a bogus website or open a harmful attachment. They are prompted to enter passwords, account numbers, PINs, and access codes to supposedly resolve account-related concerns.
Impersonating a friend, an attacker may ask for usernames and passwords of your social media accounts. In reality, the attackers will use your personal details to access your credit card information, bank accounts, or Social
Harvest information
Let’s suppose a victim clicked on the link and the keylogger was successfully installed on their computer by cybercriminals. The next step is to watch for the login credentials in the hourly burst of keyboard data. The keylogger automatically sends the information to the spear phisher’s server.
When they log into their workstation, the scammers then get the hashes of every network password, crack them, bypass
Spear Phishing vs. Phishing
While regular phishing and
Another difference is that
In phishing, campaigns have no specific targets. Attackers send random emails containing malicious links or attachments to an email contact list.
Attackers are aware that not all messages will be delivered. Some emails will be blocked by
Specific targets are not required because the attackers are aware that some of the receivers would fall victim. They know that there will be a group of vulnerable users because they are either ignorant, or too busy or lazy to see the signs.
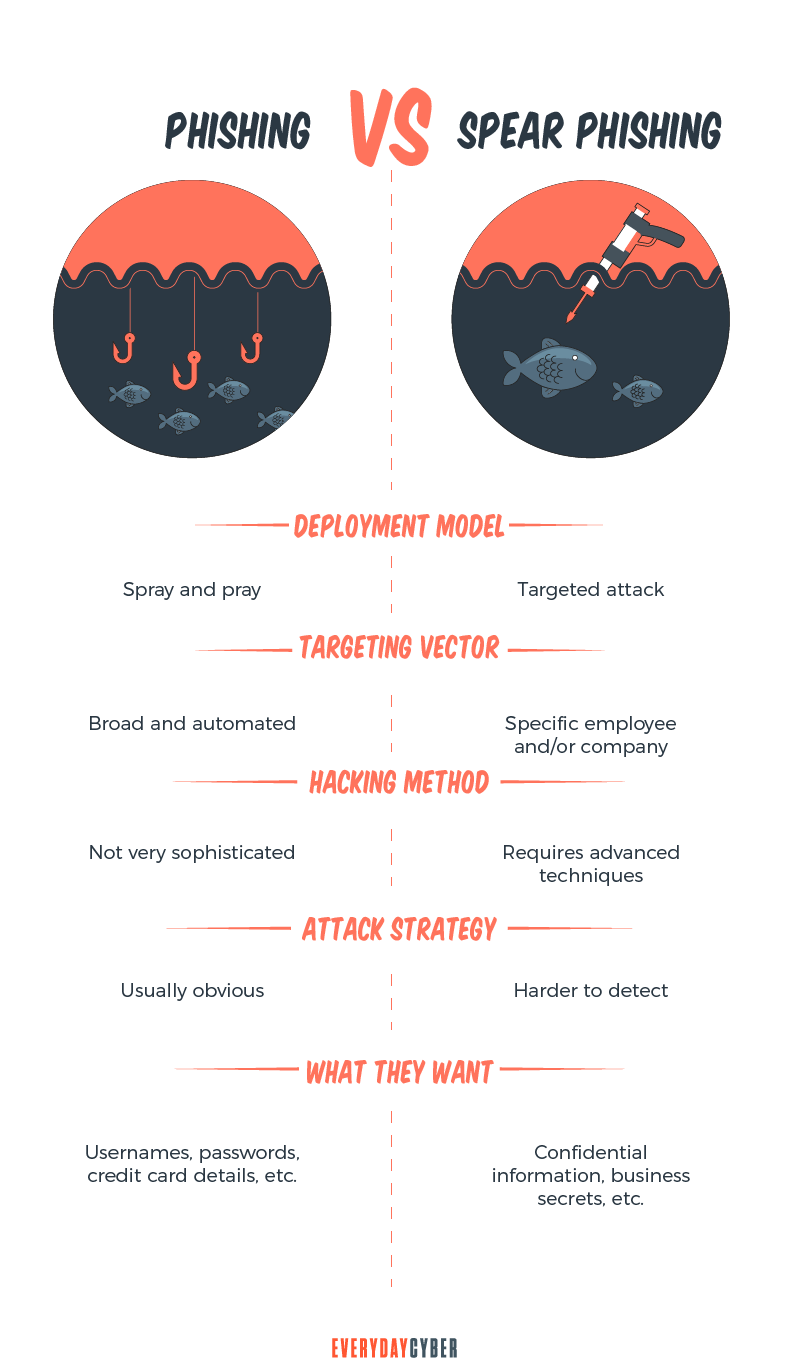
In spear phishing, scammers use a more personalized approach. They typically target highly privileged users within a business, including C-level executives, human resources workers, and accountants.
The attackers need much more research and time to be able to create what messages will work. To be more effective,
How to Protect Yourself from Spear Phishing
The best defense is a strong offense. While there’s no foolproof tool that can stop
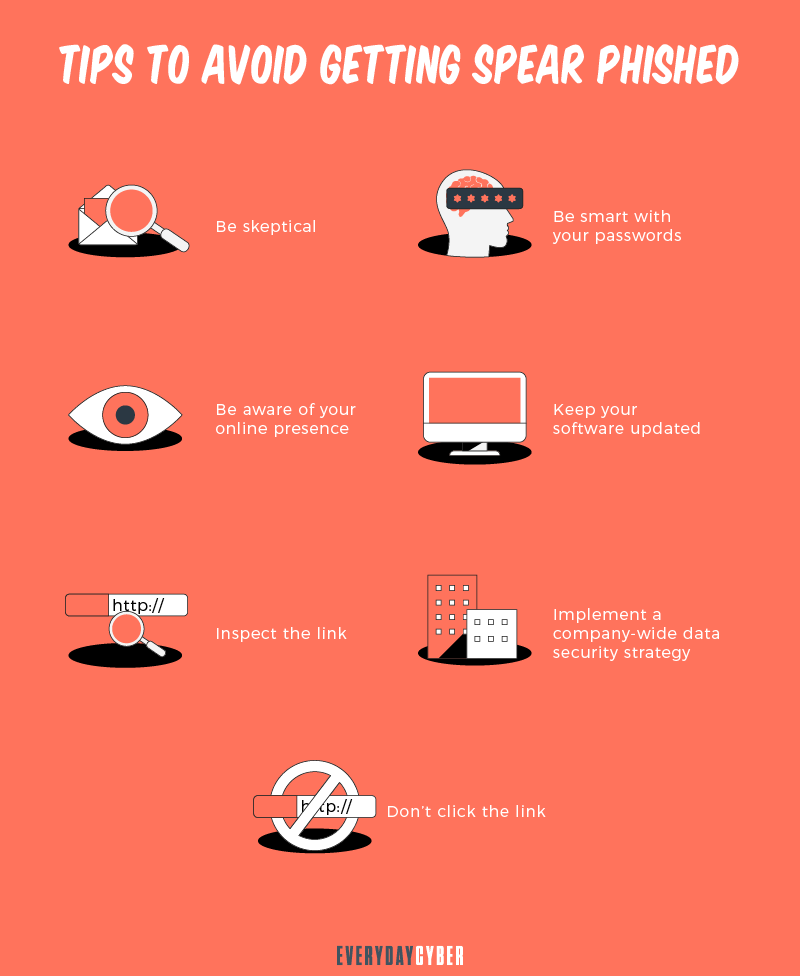
Here are effective ways to protect yourself from
1. Use email security software
Your best hope for defeating
2. Enforce tight password management practices
Don’t use the same password or password variations for all of your accounts. Use unique, long, and strong passwords that include random phrases, numbers, letters, and symbols.
Security systems are as strong as the passwords people use. Consider the following password best practices:
- Use password management software
- Avoid password sharing
- Create password complexity and set minimum length standards
- Change passwords upon reaching a set maximum password age
3. Enforce multi factor authentication (MFA)
Enabling multi factor authentication in email accounts makes them much more secure and difficult to hack. It could seem inconvenient, like when you have to run for your cell
Even if a hacker has your username and passwords, they will be thwarted if they lack the third or fourth verification stages.
4. Encrypt all sensitive corporate data
Encrypting files is a good way to shield private company data from prying eyes. The files you transfer to your systems, cloud environments, business partners, and remote places will be safer with encryption. It makes it more difficult for outsiders to decrypt your data even if they get their hands on it.
5. Do regular backups and install the latest security patches
The significance of installing
6. Provide continuous security awareness training
It takes time to educate staff members about
Consider including cybersecurity knowledge in new employee orientation procedures and reference materials. To keep your sensitive data and systems secure, regularly conduct refresher training for all staff members, including management.
Our Final Thoughts
Data breaches caused by
By entering your email address you agree to receive emails from EveryDayCyber. We'll respect your privacy and you can unsubscribe at any time.
Recommended Reading
What is Spear Phishing?
Spear phishing is a targeted cyberattack to steal your information. You should be aware of the dangers of this and how to address them.
What is Phishing?
Phishing is a cyberattack that attempts to trick people using email, text messages, phone calls, or even fake websites into giving away sensitive and confidential information.
What is ATM Skimming and Ways to Protect Yourself
ATM skimming can lead you to losing all your money in your bank account. Here's how to protect yourself from it.
How to Build a Cyber Security Awareness Program for Your SMB Business
Building a cyber security awareness culture should be a top priority for your organization. Every manager, department, and individual in your firm must commit to this on a long-term basis.
What is a zero-day threat?
A zero day threat is a security flaw known or unknown to the software vendor which hasn't had a patch made to fix the vulnerability.
What is Catfishing?
Catfishing is a deceptive technique individuals or criminal entities use to create a fictional personas or fake identities online and use them to scam unwitting victims.


