Cybercrime is not just about using sophisticated technology to launch malicious activities. Most people associate it with some techies remotely accessing computer systems to steal sensitive data for illegal purposes.
It’s also not about running away with someone else’s laptop or smartphone to gain access to a bank account and credit card credentials to steal money or
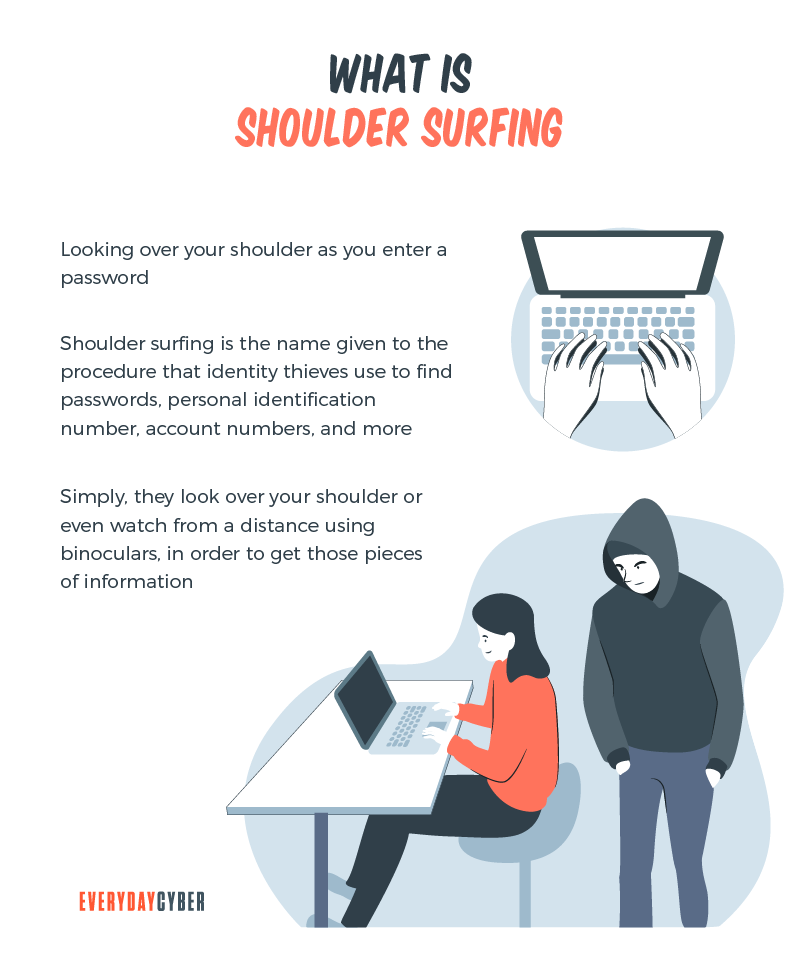
In fact, a fleeting look over the victim’s shoulder is enough for cybercriminals to get hold of usernames, passwords and other login credentials. This is the essence of shoulder surfing. As simple as it may seem, this overlooked practice can pose a real danger to individuals and businesses.
What is shoulder surfing?
Shoulder surfing is a form of social engineering. So before we can understand what shoulder surfing is, let’s delve a bit into social engineering.
In cybercrime, social engineering is a technique of manipulating people by exploiting human error, lack of knowledge and weakness to gain access to sensitive information. Attackers instill heightened emotions in their victims, such as:
- Fear
- Anger
- Curiosity
- Excitement
- Sadness
- Guilt
An enhanced emotional state, coupled with urgency and trust, makes people take irrational or risky actions, such as revealing sensitive personal information.
So what is shoulder surfing?
Shoulder surfing is a form of social engineering that enables cybercriminals to gather information just by looking over their victims’ shoulders. The aim of shoulder surfing is to obtain personal data, such as usernames, passwords or personal identification numbers (PINs), bank account numbers or credit card numbers.
How does shoulder surfing happen?
A shoulder surfing attack works in two ways: at close range or from a longer range.
Close range attempts are pretty straightforward and attackers don’t need technical skills to perform this method. Using their prying eyes, shoulder surfers simply, but covertly, observe another person’s computer or device screen or keyboard to obtain sensitive information. As the victim enters information onto the device, the attacker is likely writing, typing or recording the information somewhere.
Long range shoulder surfing attacks happen when observation is done from afar. This necessitates the use of binoculars, miniature cameras, video cameras, or
Whether close or long range, shoulder surfing can happen in the workplace or in public places like coffee shops, bars, restaurants, hotels, airport lounges or ATM queues.
Attackers can also use the shoulder surfing technique when people give their personal information in
By entering your email address you agree to receive emails from EveryDayCyber. We'll respect your privacy and you can unsubscribe at any time.
What are the types of shoulder surfing?
Shoulder surfing has two types.
Direct observation. This type of attack happens when a shoulder surfer looks directly over the shoulder of the victim and peeks into the victim’s device to obtain information, such as bank account or credit card credentials.
Recording. In this type of shoulder surfing, the victims are recorded on video to be analyzed at a later date to extract the desired information.
Shoulder surfing long predates laptops and cellphones. It goes back to when criminals spied on pay
Some examples of shoulder surfing
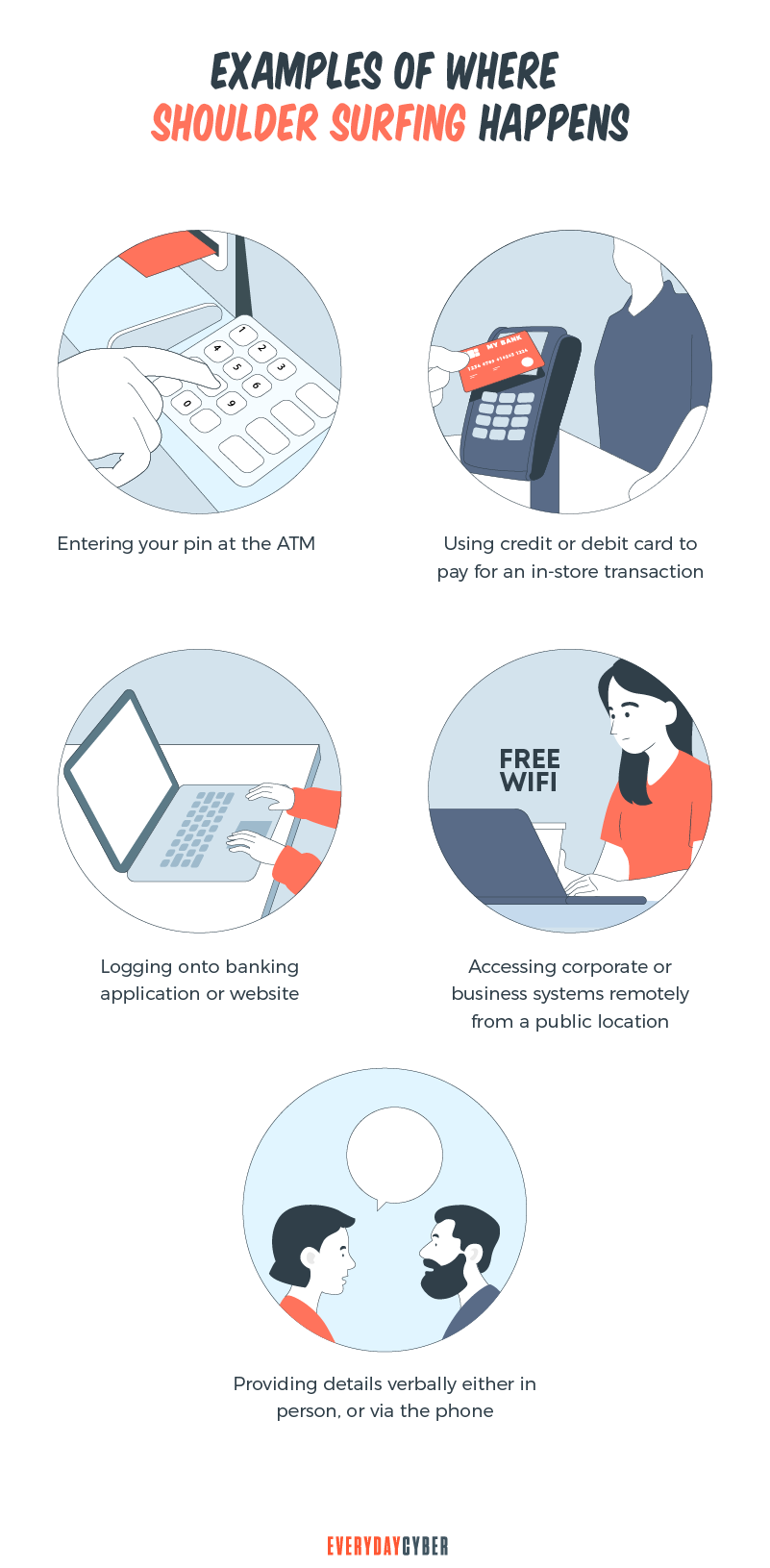
Shoulder surfers can strike in several ways. Most shoulder surfing attacks happen at ATMs and kiosks. Some can happen at crowded places where criminals have the advantage of being unrecognized. Here are some examples:
- Providing details of sensitive information verbally or via the
phone - Entering your PIN at an ATM
- Logging in to a banking website using a laptop or
mobile device - Using a debit or credit card to pay for your purchases at a store
- Accessing company systems remotely from a public location
- Handing over your credit card at a cash point
- Accessing your bank account in the workplace while coworkers look
- Entering the PIN of your door while a snooper is around
- Logging in to your laptop or
mobile device while sharing a table with a stranger
What are the consequences for shoulder surfing crimes?
For the victims, the consequences can be heavy financial losses, stolen identities, hijacked accounts and compromised
There are consequences as well for shoulder surfing attackers. Stealing an individual’s bank account, credit card account or digital
Shoulder surfing crimes can also lead to civil damages awards to compensate victims. In many cases, the organizations where the crimes happen are required to update their
Steps for preventing shoulder surfing
Set up a privacy filter
A privacy filter, or computer privacy screen, is a thin sheet of plastic that’s placed over your monitor or display panel to prevent prying eyes from seeing information. It limits visibility to only the person seated directly in front of the computer. Anyone attempting a glance from the left or right will only be able to see a black screen.
Tilt, incline, slant or shift your device
This technique is especially effective for smartphones. Depending on where the unwanted gaze is coming from, you can simply set an angle for your device to block the visibility of intruding eyes. For laptops and tablets, you can tilt the screen downwards slightly or close your laptop to take a break.
Block their view
Take this more proactive move if you’re protecting sensitive work documents. You can use a free hand to cover the side of your smartphone that contains the important data. If you’re using a laptop, cover the side of the screen that needs protection with a cardboard sheet, a book, a piece of cloth or anything that can block the view of unauthorized individuals.

Sit out of view
When working remotely in a public place, such as a coffee shop, make it a point to find a seat against a wall to keep away all those wandering eyes in front of you. Make sure the wall isn’t mirrored or all glass. If you’re sitting outside, try to avoid the crowd and set against a solid wall.
Maintain awareness of your surroundings
Watch for people, recording devices and other unwanted movements. Visual hacking is simple, quick and goes unnoticed so be very vigilant of your surroundings.
Use password manager
A
Protect your PINs
Create a PIN that’s hard guess. Memorize it and keep it secret. Always shield your PIN when using an ATM by using your freehand, a purse or magazine to cover the keypad. Watch for people lurking while you’re at the ATM.
Avoid using public networks
Free public Wi-Fi systems are usually poorly configured and are prone to hacking and other cyber attacks. They are also often unencrypted, making it easy for criminals to hack them. If you must use a public Wi-F-, we recommend that you use a virtual private network or
Set strong passwords
Create strong passwords that can’t be cracked by brute force, dictionary attack or phishing. The best passwords are long and contain a good mix of letters, numbers and symbols, yet easy to remember. Avoid common substitutions and memorable keyboard paths like “qwerty”. Avoid reusing passwords that can lead to the compromise of one being the compromise of all.
Use biometric authentication
Biometric authentication is the strongest physical
Use two-factor authentication
Two-factor authentication is a
Use contactless payment methods
A contactless payment method refers to a secure way of paying for products and services using a debit, credit, smartcard or other payment devices that applies radio frequency identification (RFID) and near-field communication (NFC). As its name suggests, there is no contact between the payment mode and the point of sale (POS) terminal. The payment takes effect when the mode of payment (debit card) is tapped near the POS.
Monitor your credit regularly
Monitor your credit regularly to get ahead of shoulder surfing. If there are transactions you don’t recognize in your credit account, immediately report the matter to the credit bureaus, particularly Experian, TransUnion or Equifax.
Our final thoughts: Shoulder surfing may seem uncomplicated, but the risks are real and ever increasing. Even with just one compromised device, the destruction can spread across all devices in the organization. As in other cyber threats, awareness, vigilance and prevention are the best deterrents of shoulder surfing and its devastating effects.
By entering your email address you agree to receive emails from EveryDayCyber. We'll respect your privacy and you can unsubscribe at any time.
Recommended Reading
Strong Passwords. One giant step to protect our digital lives
Here's how to create long, complex, and unique passwords to protect your accounts and keep your sensitive info safe from hackers.
10 Cybersecurity Trends for Small Businesses in 2022
Knowing the latest cybersecurity trends spells the difference between keeping your business safe and opening it up to cyber attackers.
What you should know about Chatbots And cybersecurity
Chatbots are conversational assistants that automate repetitive chores. We like them because they assist them in completing jobs swiftly and without the need for human interaction. But an unprotected chatbot can be a security problem. Hackers can use defenseless AI chatbots to carry out nefarious activities. Read to learn more.
What to do if your email Is hacked
Identity theft and bank account or credit card fraud are both possible consequences of a stolen email. If you suspect that your email has been hacked, act quickly to limit the harm. Here are 9 steps to take back control of your email if you have been hacked.
What is a Password Manager?
A password manager is an encrypted storage system for keeping and managing passwords usually protected by a master password. Some password managers use biometric data to protect the vaults instead of master passwords. Still others support the use of two factor authentication for higher security.
What is a Computer Virus?
What's a computer virus? We hear about it all the time but do you really know what it is and how to prevent one?


