The term Zero Day Threat can be confusing to a lot of people. It sounds like an action-packed thriller movie but I can tell you it is definitely not a thrill to be impacted by one. It is definitely a term that originates out of the bowels of cybersecurity but it represents one of the scariest cyber vulnerabilities to computer systems, digital devices and the digital infrastructure that runs our lives is faced with.
A zero-day threat represents a vulnerability in digital technology, most notably software, that is exploited and discovered on the same day. Zero Day represents the age of the exploit, which takes place before or on the first (or “zeroth”) day of a product and/or
So what is a Zero Day Threat, Really?
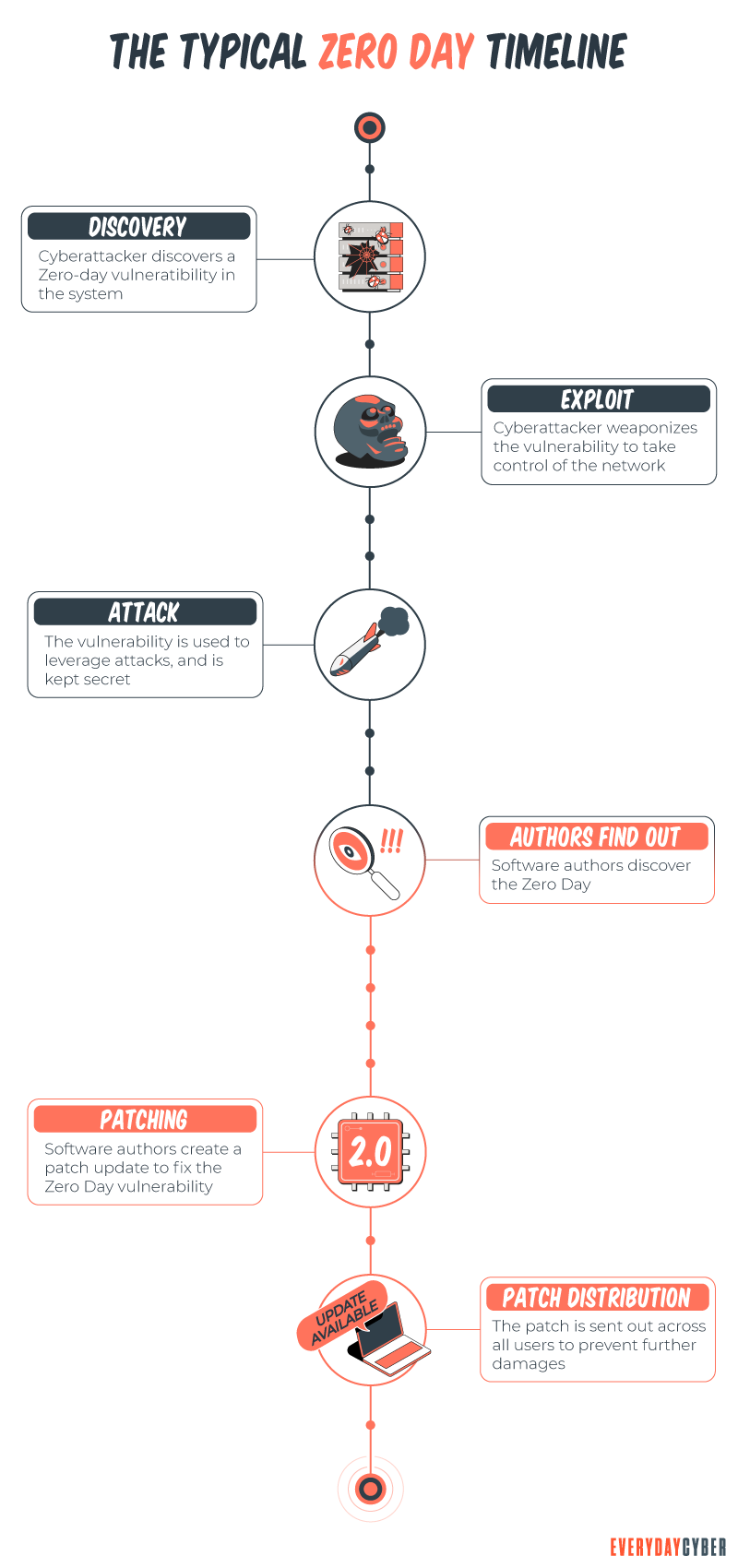
A zero day threat is an attack vector that is known only to the attackers, so it can work without interruption from the software create or users. It is a flaw in a piece of software, or even sometimes hardware. The typical lifecycle of an attack utilizing zero days to compromise devices:
- A vulnerability or new attack vector is discovered by a malware creator
- The capability is weaponized and proven to work by the hacker
- Zero day vulnerabilities are kept secret and utilized by bad actors
- The vulnerability is discovered by defenders
- The software or hardware manufacturer or application vendor delivers a patch
- The zero day is no longer a zero day

Bad actors are constantly looking for, testing, and seeking vulnerabilities in our digital lives. It is also possible that even regular users discover these vulnerabilities and warn other users and the company who built the technology – often broadcasting the find over the internet. Once the vulnerability is discovered, it is a race for the hackers to exploit the vulnerability and the companies making the product to fix it.
That’s what makes zero-day threats so dangerous for us today. Hackers are very sophisticated and work very fast. Once they discover a vulnerability or one is identified through public forums, say via a user, they can and do move very quickly to exploit it. It’s a constant battle for companies building software and hardware to stay ahead of the criminals.
How to protect yourself from a Zero Day Threat?
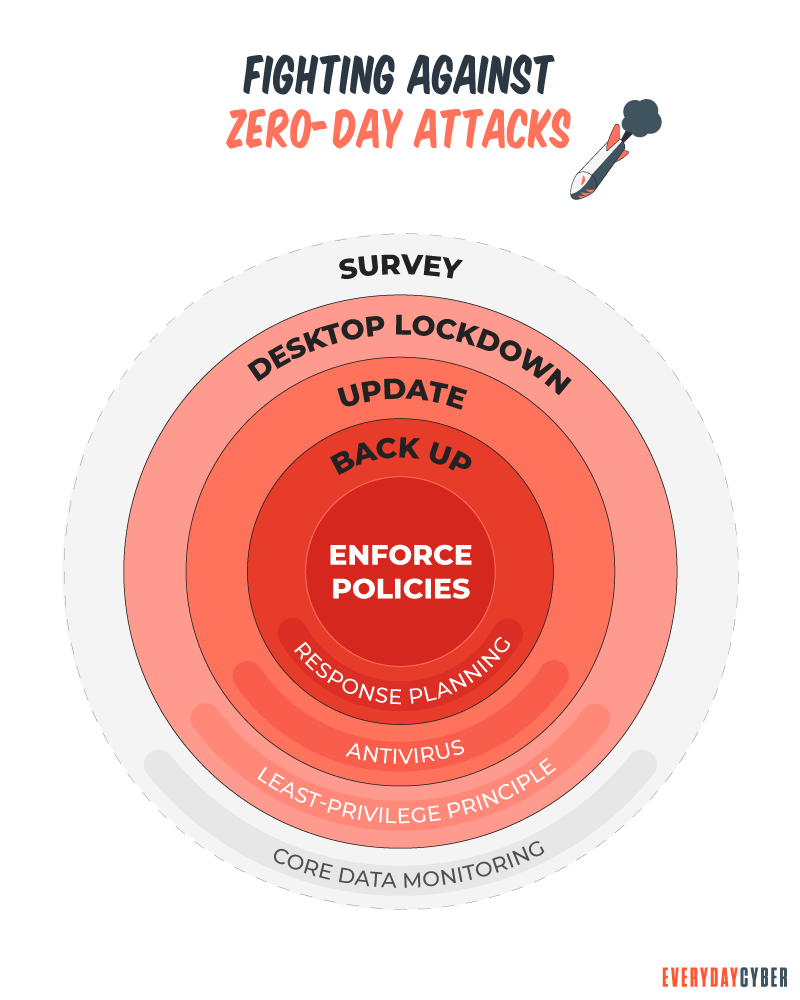
While zero-day attacks make us all vulnerable, where they are most dangerous is long after a
-
- Update your browser, operating system, and applications – applying patches closes the exposures in your software and operating systems, strengthening your resistance to malware.
- Do NOT click on links in unknown emails or download unknown attachments – #1 rule of good cybersecurity hygiene and an effective method to protect against zero-day attacks.
- Use only essential applications– the more apps you have installed, the greater the risk to malware. Reduce the risk to your network by using a minimum of applications.
- Be careful which website sites you visit – Consider using a safe search tool that will warn you of risky sites in your browser search results and prevent you from going to malicious sites.
- Get quality antivirus/antimalware tools – invest in a comprehensive
security solution.
Stay vigilant and fight against cybercrime.
The first rule of good cybersecurity and digital protection is simply to apply common sense – “check twice, click once”.
By entering your email address you agree to receive emails from EveryDayCyber. We'll respect your privacy and you can unsubscribe at any time.
Recommended Reading
The #1 Cyber Threat Small Businesses are Facing
Phishing attacks are the most widespread and most damaging threat to small businesses, accounting for 90% of all cyber security breaches.
What is Two Factor Authentication
Two-factor authentication is a security mechanism in which individuals provide two authentication factors to log on to their account. Using a username and a password to log in to an account is in itself a 2FA. So is withdrawing cash from an ATM using your ATM card and a PIN.
What is a Keylogger?
Keylogger is a digital surveillance tool. They can track every click, touch, key stroke, download and conversation carried out on the device they are installed on
10 Cybersecurity Trends for Small Businesses in 2022
Knowing the latest cybersecurity trends spells the difference between keeping your business safe and opening it up to cyber attackers.
What is DNS Hijacking?
DNS hijacking is no laughing matter. It is a serious security threat that is consuming the cyber world. The critical role of DNS for network security has made a primary target for facilitating mass data theft.
What is HTTPS?
HTTPs enables web servers and web browsers to establish secure connections. It encrypts data being transmitted in both directions. This helps prevent thieves from stealing sensitive information along the way.

