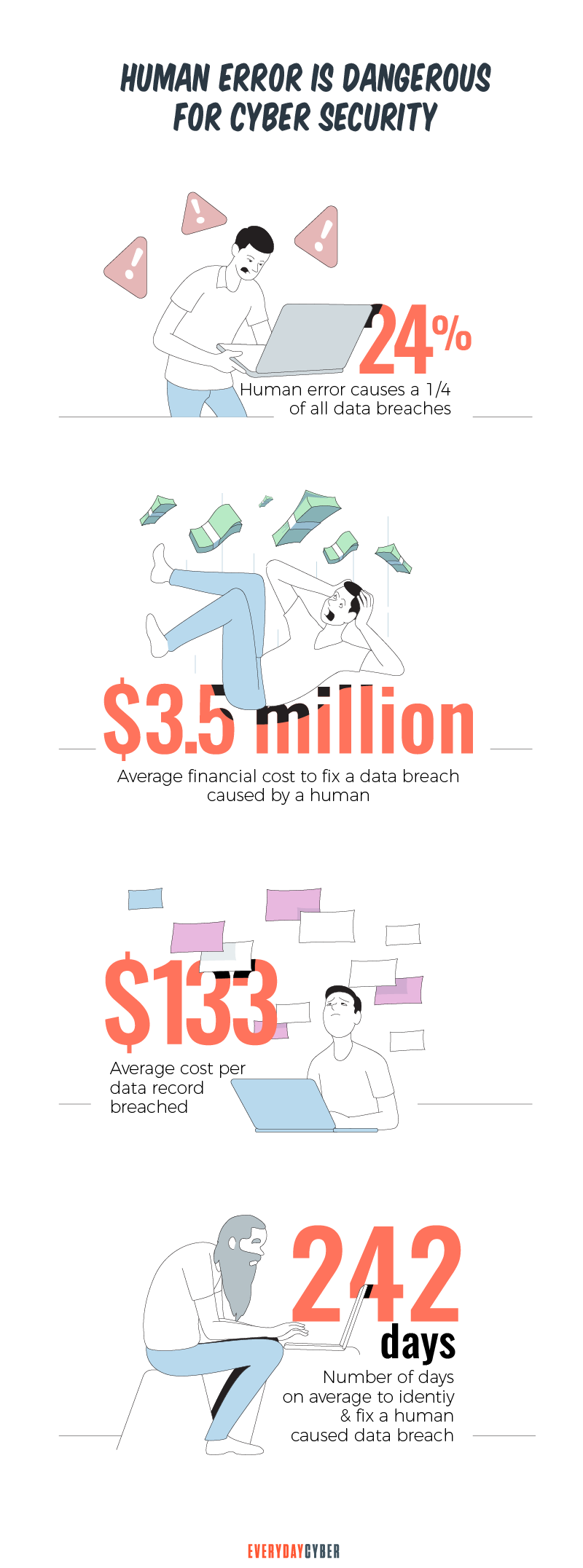
Majority, or 54% of small business owners, think they’re too small for a cyber attack. Yet, 43% of cyber attacks target small businesses. You don’t want to be part of that statistic, do you?
This happened in 2019. The numbers are expected to go even higher due to the chaos brought about by the Covid-19 crisis.
As if those figures are not enough, small businesses struggled in other cyber
- New small business cyber breaches increased by 424%
- A weak, default, or stolen password was used in 63% of confirmed data breaches
- 54% of small firms did not have a plan in place to respond to cyber threats
- Following a cybersecurity incident, 65% of small businesses failed to take action
- 83% of small firms did not have funds set aside to deal with a cyber
security threats
These alarming numbers require businesses to make cybersecurity a priority. But it seems that small businesses are ignoring the need for a

Why Do Cyber Criminals Love to Target Small Businesses?
Mind you, criminals are getting their cue from statistics. Now they know that most small companies don’t take cyber
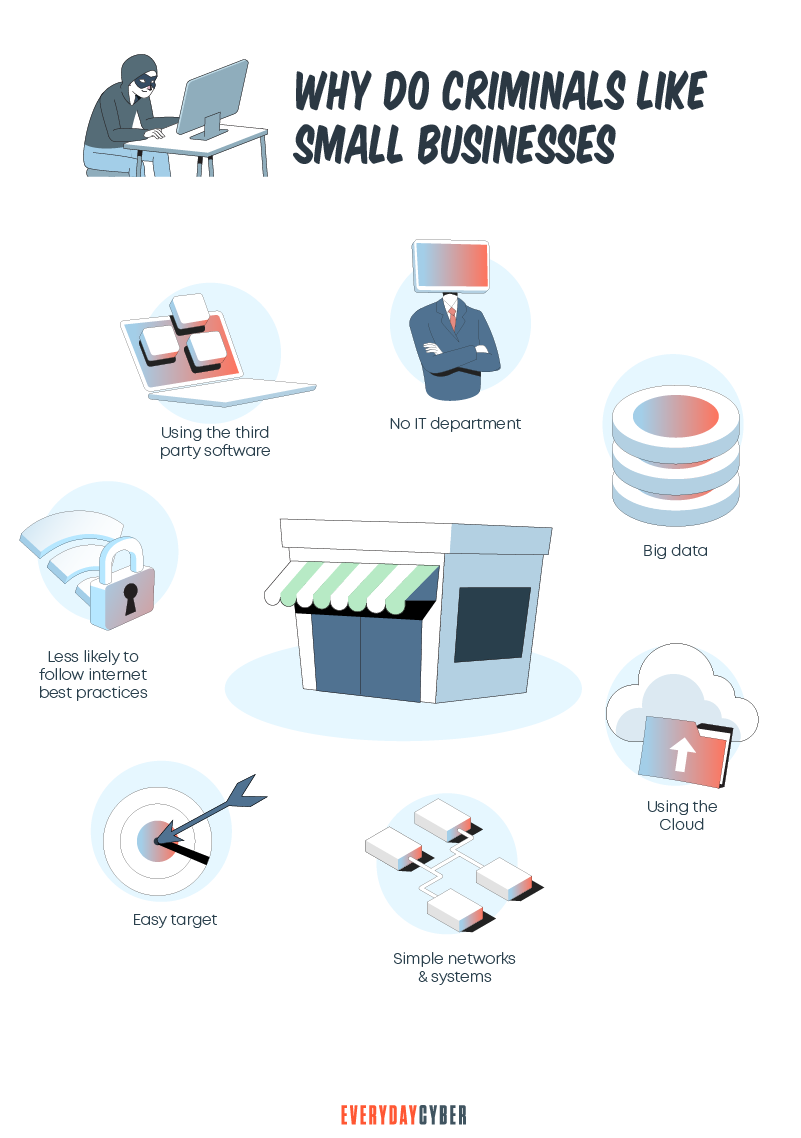
Hackers love this scenario. With weak passwords, they can easily gain access into systems. Hackers can also manipulate and force small businesses with no recovery plan to pay ransom. Ransom is relatively cheaper than the cost of data loss.
Cyber attackers also infiltrate small businesses and use them as entry points to their bigger targets. This was what happened in the 2013 Target cybersecurity breach. Cyber criminals compromised the credentials of an HVAC company doing business with Target. The criminals pushed their malware to Target’s point-of-sale devices. They were able to steal 40 million debit and credit card accounts of Target customers.
Small businesses can do a lot to better safeguard themselves. And they don’t even have to shell out large amounts of money to do so.
Understand Your Small Business
Why do companies need cybersecurity? So they will be able to innovate and grow more quickly in a secure way.
Your
What do you want to achieve in this
Before going into the key details of your cyber
Take time to understand your business. What is the current status of your infrastructure, technology, and the level of cyber
IT Infrastructure and technology
Your IT infrastructure includes hardware, software, applications and data systems. Data
Tools and strategies to help businesses and individuals improve their cyber-resilience are also part of the IT infrastructure. These components all help prevent or withstand
Your people
Your people are your first line of defense in cyber
Every person in your organization has a role to play – from the top to the bottom. Are they ready to thwart any attack attempts? Have you trained them enough to be able to deal with unexpected cybersecurity threats?
Management should develop a culture of leading from the top. What can you expect from employees if their bosses are oblivious of what people under them are doing?
Risks, threats, and vulnerabilities
Risks
Complete
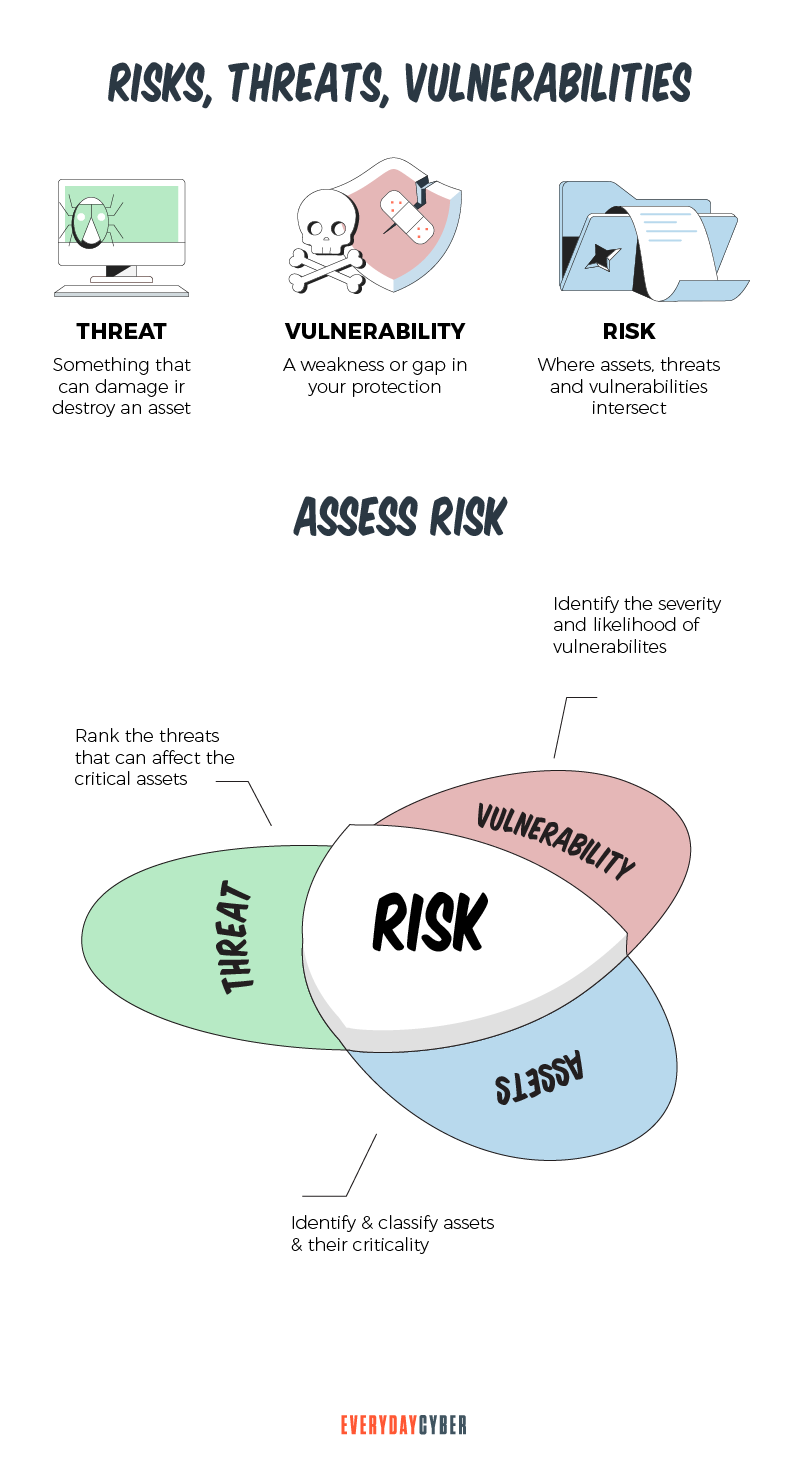
Threats
Exploring the types of cybersecurity threats is part of identifying your dangers.
There are hundreds of them, but you’ll need to reduce them down to the ones your business is most vulnerable to. For instance, you’ll need to determine the potential threats to your financial, e-commerce, or healthcare business. Phishing and social engineering tactics are common network
Vulnerabilities
Vulnerability is susceptibility to possible threat exposure. This may come in the form of flaws in the system, unprotected vectors, or human error. You may need outside assistance for your vulnerability assessment.
Likelihood of occurrence
The likelihood and frequency of occurrence will depend on the
By entering your email address you agree to receive emails from EveryDayCyber. We'll respect your privacy and you can unsubscribe at any time.
10-Step Cyber Security Plan
Now that you’ve assessed the current state of your
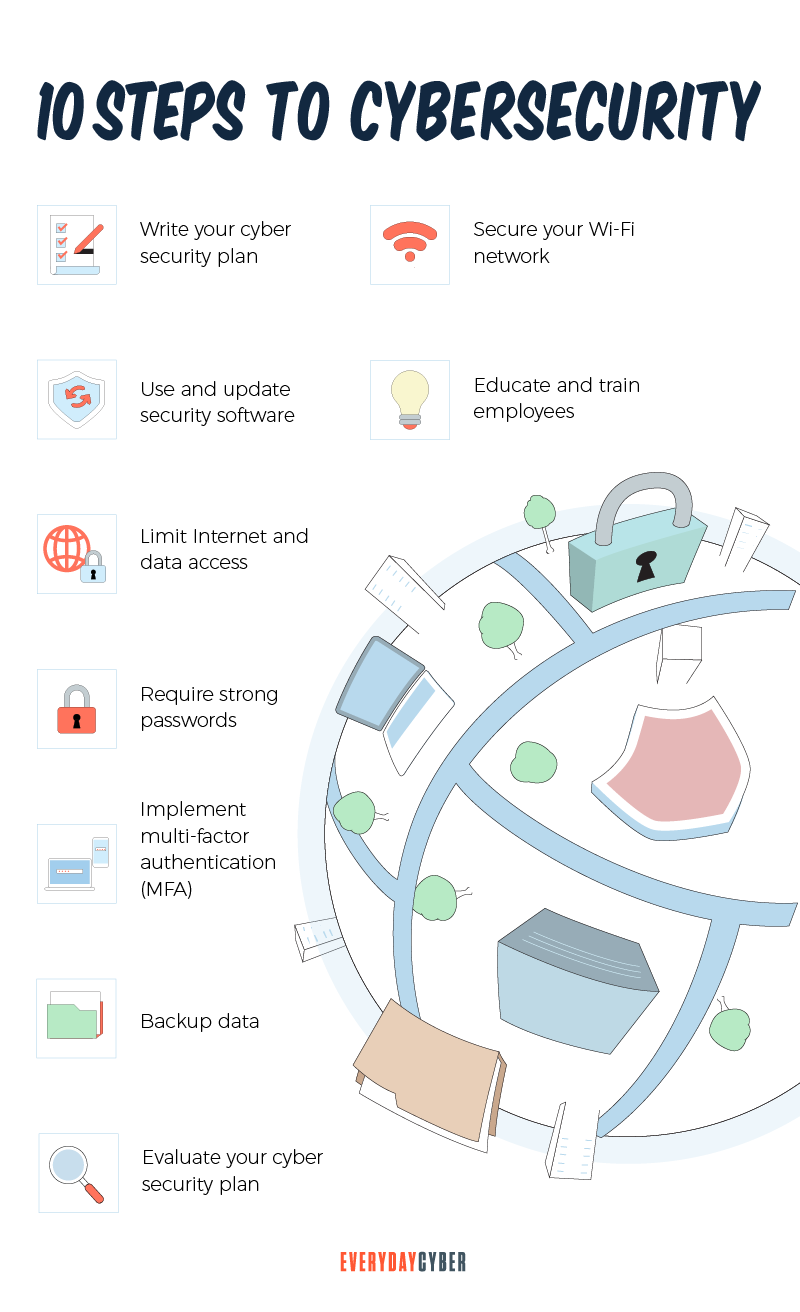
1. Write your cyber security plan
An effective cyber
An important step in documenting your plan is crafting work conditions that are acceptable to your employees. Why?
No matter how robust the
2. Secure your Wi-Fi network
No matter how good your
Your internet service provider and router manufacturer may be able to supply you with features or information to help you secure your wireless network.
Change default passwords on just about every router in your network. Someone who knows the default passwords could reconfigure your routers.
Ensure that the firmware is up to date. Firmware is a low-level software that runs a router. It establishes your network’s
If you have visitors who want to access your Internet connection, let them use the guest network, if available. It’s not like your visitors are hackers, but it’s always better to be on the side of caution than be sorry later.
And don’t forget the good old firewall to protect your network perimeter. A properly configured one will help detect malicious access and restrict outbound traffic to prevent data landing on the wrong hands.
3. Use and update security software
Security software is an application that protects servers, routers, devices and the entire network. It helps fix software bugs, enhance features, and solve compatibility issues. More importantly, it irons out
When you install
Many of the data breach attacks use software flaws in operating systems, browsers, and common applications. These are large programs that need to be updated on a regular basis to stay safe and reliable. Instead of putting off software upgrades, consider them one of the most important activities you can do to secure your business online.
4. Educate and train employees
It’s crucial that you educate employees about cyber threats. Employees who aren’t trained to recognize and avoid cyber risks greatly increase the chances of your small business being hacked.
It’s critical that everyone in your company develops a “security culture”. That is, a mindset in which they are always aware of attack vectors. These could be questionable emails, pop-ups, malicious links, and suspicious download requests.
It’s also important to give special training to key personnel who handle sensitive data and responsibilities. They could be C-Suite or mid-level executives, specifically those in finance departments.
Classroom training, training videos, and simulated phishing tests are among the various
5. Limit Internet and data access
Depending on the type of business you run, try to limit access to the Internet.
Allowing employees free Internet access can lead to a significant drop in productivity. Malware and ransomware downloads are also more likely when you have unrestricted Internet access. Inappropriate Internet use at work might result in a slew of legal issues.
Many businesses employ web filters to enforce appropriate Internet usage and prohibit access to dangerous websites to avoid the hazards involved.
Many businesses do not discriminate between sensitive data and information that is available to the public. If an attacker gains access through a weak link, they have the keys to your entire database. If you don’t limit access to data depending on who truly needs it, you’re opening yourself up to a far bigger attack surface.
Sort your data into categories. Protect sensitive business data, and only authorized workers with a legitimate need for it should have access to it.
If you must send important information through a less-trustworthy network, make sure it’s encrypted. Authentication is used to ensure that the person who is accessing the business data is who they say they are. Make audit logs that can be checked for unusual activity. If you want to avoid a sensitive data leak, you must limit data access to only what is required for each job role.
6. Require strong passwords
Passwords are your network’s first line of defense against unwanted access. Your computers will be safer from hackers and bad malware if you require all users to use strong passwords.
Password guessing is one of the most prevalent ways for hackers to get access to computers. Intruders can quickly access and control a digital device using simple and widely used passwords.
On the other hand, a tough-to-guess password makes it almost impossible for regular hackers to break into a machine. Strong password best practices are your best bet to force hackers to hunt for other targets. The more difficult the password, the less likely it is that an unwanted intrusion will occur on a computer.
7. Implement multi-factor authentication (MFA)
Passwords are the first lines of defense, but hackers can easily guess simple passwords. Multi-factor authentication is a second line of defense if the first line fails.
Forbes recently reported that there are 15 billion usernames and passwords circulating in the Dark Web taken from 100,000 data breaches. Are yours one of them? You never can tell.
More and more organizations are embracing MFA because it:
- Enables stronger authentication
- Adapts to emerging threats
- Offers
security without disturbing user experience
8. Backup data
We only need to read the news to be aware of the growing threat of cyber attacks. The year 2020 saw the highest increase in cybercrime yet, thanks in part to the growing popularity of work-from-home jobs.
Corporate breaches appear to be the most conspicuous, but no firm is completely protected from risk. Small firms are generally seen as easy targets by malicious actors due to their weak

How quickly will you be able to recover if your company suffers data loss as a result of a breach? To secure your critical data, you need to backup data. Even if data backup does not prevent you from a cyber attack, it will help you recover as quickly as possible.
9. Evaluate your cyber security plan
Cybersecurity audits serve as a review of the policies you’ve set forth in your
Audits also help businesses take a proactive approach when crafting cybersecurity policies. Threat management thus becomes more dynamic and relevant to the current threat landscape.
Ideally, cybersecurity audits should be carried out by third-party providers in order to eliminate any conflicts of interest. Third party auditors come with a different view of your environment and can oftentimes spot things you don’t see.
But an in-house team may also do it as long as they act independently of their parent organization.
10. Incident response game plan
An incident response plan is essentially a cybersecurity strategy for what to do if your company’s
Your firm is going to suffer a cyber event at some point, regardless of how hard you work to secure your organization or how vigilant your staff are.
How well you train your incident response team to respond to the catastrophe can determine how long your firm survives.
For example, if your customers’ credit cards are stolen, you’ll need to:
- Inform all affected customers
- Request customers to check their statement
- Advise your customers to report the incident to their credit card companies immediately
- Instruct your customers to replace their credit cards, or change passwords, PIN codes, and login credentials
What you might do is create theoretical incidences that may potentially happen. Plan several effective cybersecurity strategies on how to respond to these threats. You never know when you will need to use them.
Our final thoughts. You should be scared of cybersecurity risks by now. Think of the economic, reputational, and regulatory costs a cyber attack brings. Your corporate network can’t defend itself against data breach operations without a cybersecurity plan. This makes you an easy target for fraudsters. You wouldn’t want this to happen. Would you?
By entering your email address you agree to receive emails from EveryDayCyber. We'll respect your privacy and you can unsubscribe at any time.
Recommended Reading
Lock the Door. Bad Passwords: The Greatest Threats to Password Security
Bad passwords are the entry way for hackers to get into your accounts. Learn how to protect your cyber assets by using better passwords now.
10 Cybersecurity Trends for Small Businesses in 2022
Knowing the latest cybersecurity trends spells the difference between keeping your business safe and opening it up to cyber attackers.
What is DNS Hijacking?
DNS hijacking is no laughing matter. It is a serious security threat that is consuming the cyber world. The critical role of DNS for network security has made a primary target for facilitating mass data theft.
Is Cyber Security Awareness Training Critical for SMBs?
You might think that cyber security awareness training is not for small businesses. You might also think that the bad guys are more interested in bigger companies. You probably should read this because you would be wrong on both counts.
What is a Hacker?
A hacker is someone who challenges technology to see if it can be compromised. A hacker can black hat or white hat.
Things About Ryuk Ransomware You Need to Know Right Now
Ryuk ransomware is one of the most dreaded malware to date. It encrypts or steals corporate data to extort millions of dollars from its victims. The Covid-19 crisis greatly influenced the recent rise in ransomware. The remote work response to the pandemic created huge gaps in the worlds cyber defenses. Threat actors saw these vulnerabilities as opportunities to spread large-scale ransomware attacks.



