Why is knowing cyber
The pandemic has compelled small businesses to shift to remote work. They have become more vulnerable to cyber
If we go by the trends, the attacks have become more frequent, targeted, and complex. Cyber criminals are always attempting to launch attacks against small businesses.
The increasingly online nature of our lives means opportunities for cyber attackers. Hackers, phishers, and cyber thieves do all sorts of cyber crimes that disrupt our lives. This is why individuals and business owners should be aware of cyber
To know or not to know
It depends on you.
The future of small businesses depends on whether they choose to know the trends in cybersecurity or remain ignorant of them.
Understanding these trends will help you secure your business today and in the future. Choosing not to know the trends will put you in a position of danger.
10 cyber security trends in 2022 that small businesses should know
Small businesses worldwide are still reeling from the effects of Covid-19. Many are moving their operations online and adopting remote work. And cyber criminals are happy about this development because they can practice their trade and target small businesses with more elbow room.
We’ve put together a list of cyber
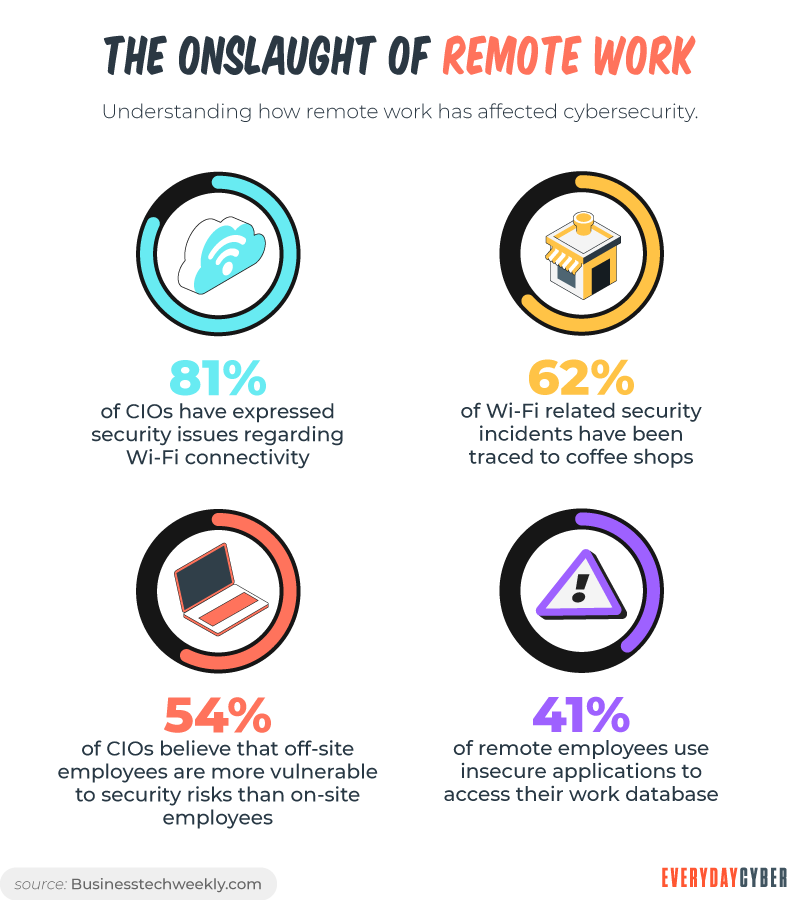
1. The rush to remote work created new threats
Small business owners decided to shift to remote work to cope with Covid-19. The shift needed to be rapid. But this left small businesses with inadequate
Remote work poses new cyber
More employees working from home are using their personal gadgets for work. The lines have gotten blurred between personal and professional use of these devices. Using personal gadgets increases the risk of mixing up personal and company information.
Threat actors take advantage of the remote work environment. They beef up their criminal tactics to cope with new
How to deal with this:
You need to patch up the weaknesses of your
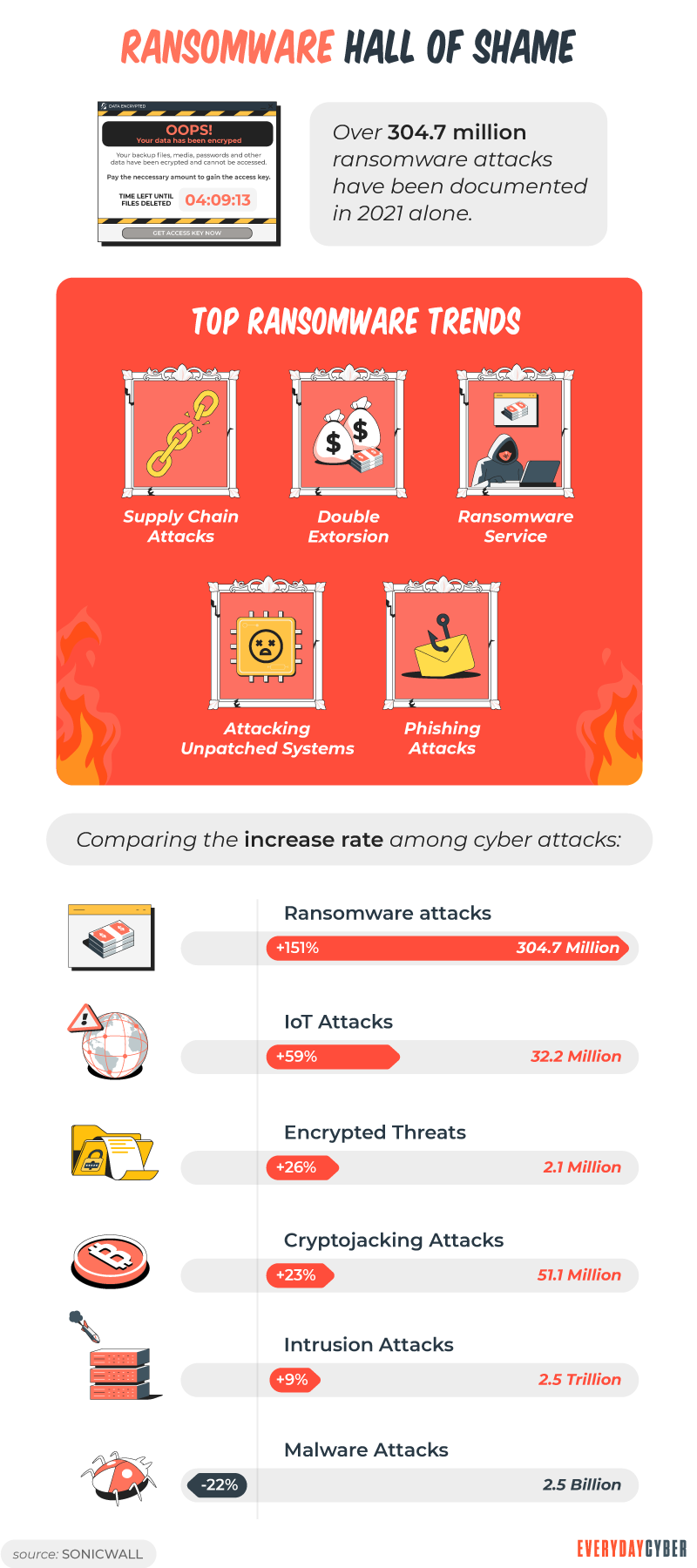
2. Ransomware continues to soar
Ransomware attacks have been around for the past two decades. But the volume of cyber attacks and the size of ransom amounts continue to rise. These attacks are becoming more sophisticated with the use of machine learning. The driving force for most cyber attacks is ransom. Attackers share their loot on the dark web with coordinated effort.
Hackers have become more adept at hiding malicious code. They use more than 120 separate classifications of ransomware, according to some estimates. The wide array of options makes it easy for cyber criminals to launch attacks. Digitization and remote work also partly contributed to the rise.
Ransomware involves breaching cyber
A Kaspersky study lists these famous ransom victims in 2020:
- Foreign exchange company Travelex (January)
- Croatia’s biggest oil company INA Group (February)
- Major electronics manufacturer California-based Communications & Power Industries (CPI) (March)
- Portuguese energy giant Energias de Portugal (April)
- New York-based law firm Grubman Shire Meiselas & Sacks (May)
- Automotive titan Honda offices in the U.S., Europe, and Japan (June)
- French telecommunications company Orange (July)
- University of Utah (August)
- Karachi, Pakistan sole power distributor K-Electric (September)
- India news agency Press Trust of India (October)
- The Brazilian Superior Court of Justice (November)
- Arizona-based healthcare organization GenRx Pharmacy (December)
The list doesn’t include small businesses. But it shows how widespread ransomware cyber attacks are. The list should also be a warning to small businesses. If the big ones can be hacked, why can’t you?
How to deal with this:
Update hardware and software regularly. Patch operating systems and browsers as a matter of practice. Have a backup plan and go back to the basics. That is, use strong passwords, multi-factor authentication, and a robust cyber
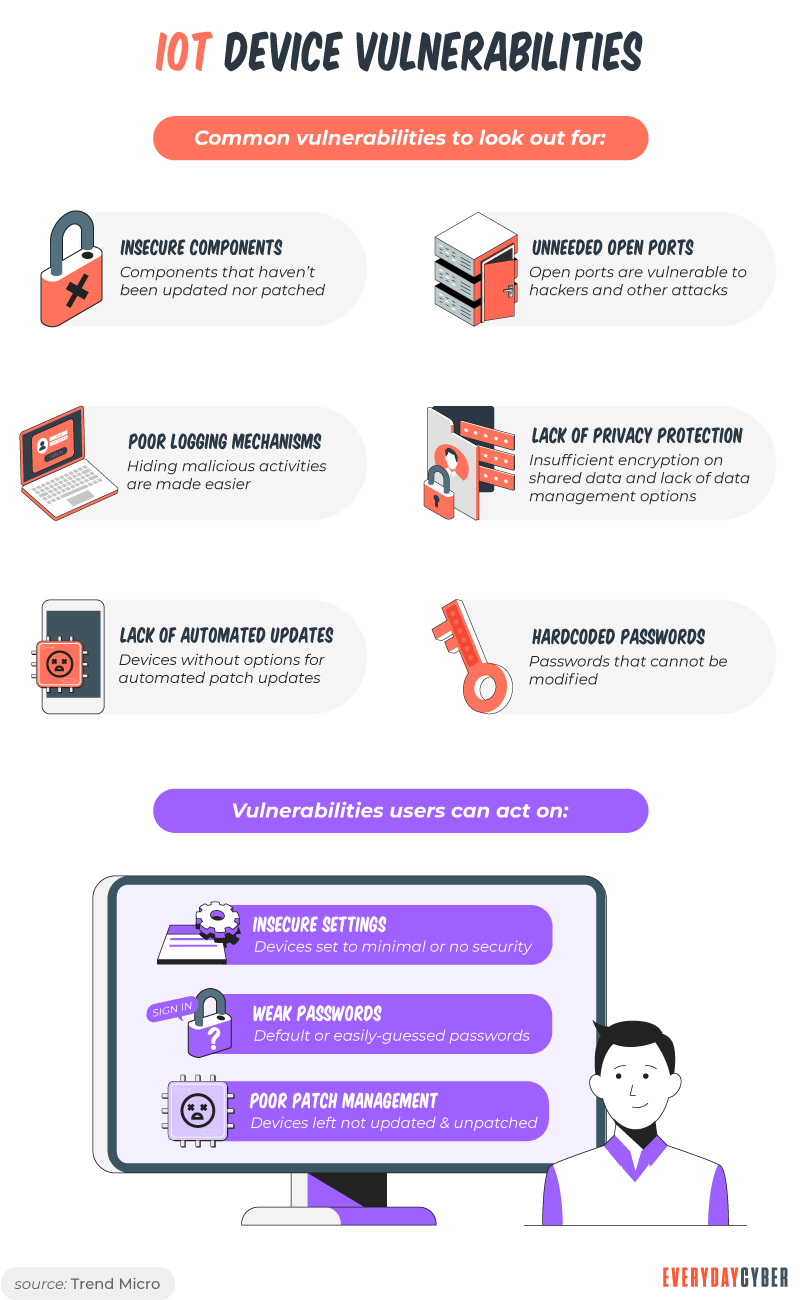
3. Cyber attacks are expanding to IoT devices and the supply chain
The use of the Internet of Things has changed the direction and size of cyber attacks. IoT devices include:
- Smart home devices
- Connected cars
- Wearable health monitors
- Autonomous farming equipment
- Smart factory machinery
- Wireless inventory tracker
IoT devices will grow faster than non-IoT machines. Research firm IoT Analytics estimates there are 21.7 billion connected devices worldwide. The report predicts that of that number, 11.7 billion or 54% are IoT devices.
The same report forecasts that by 2025, the total number of IoT devices will reach more than 30 billion. Each person will own almost four devices.
The goal of hackers is to breach these networks through third parties. They may be contractors, partners, customers, and other components of the supply chain.
The unprecedented use of IoT creates supply chain vulnerabilities. Hackers use certain techniques to exploit the weakest links in the chain.
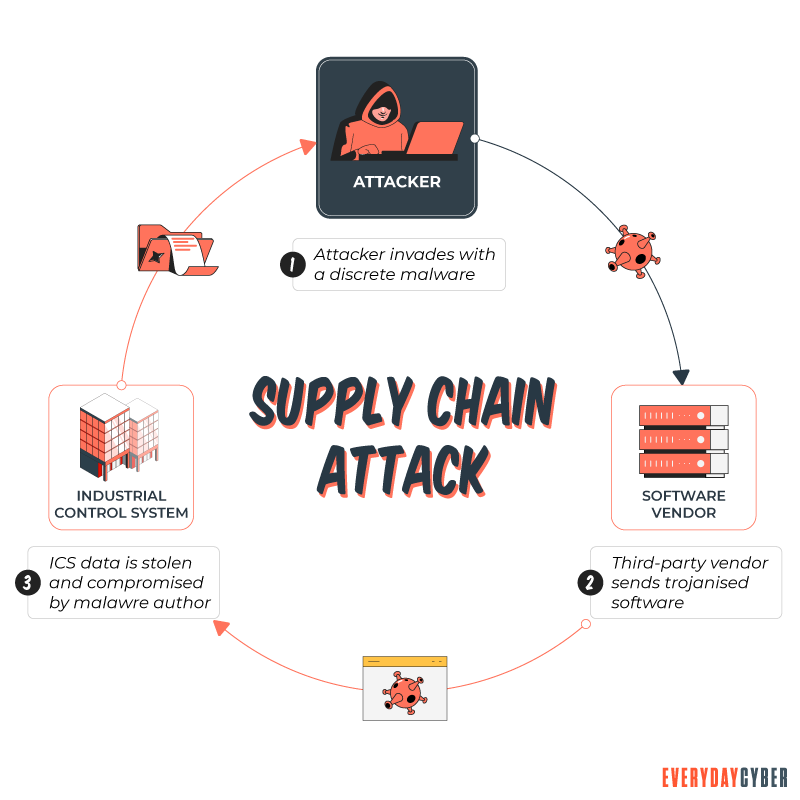
They first identify poor
How to deal with this:
Business owners should develop a strong endpoint
4. Increased cloud services mean increased cloud security threats
Cloud services are becoming popular with small businesses. They offer a range of benefits, such as efficiency, scalability, and lower costs. The rapid adoption of remote work also increased the need for cloud services.
The move to cloud computing was drastic. It gave small businesses little time to prepare their infrastructure. They also came unprepared because of limited resources.
Another drawback is the inadequacy of some cloud services. Some providers cannot provide secure encryption and authentication. Others lack proper configuration and audit logging services. Some others fail to isolate the data of tenants from each other because they are sharing space in the cloud.
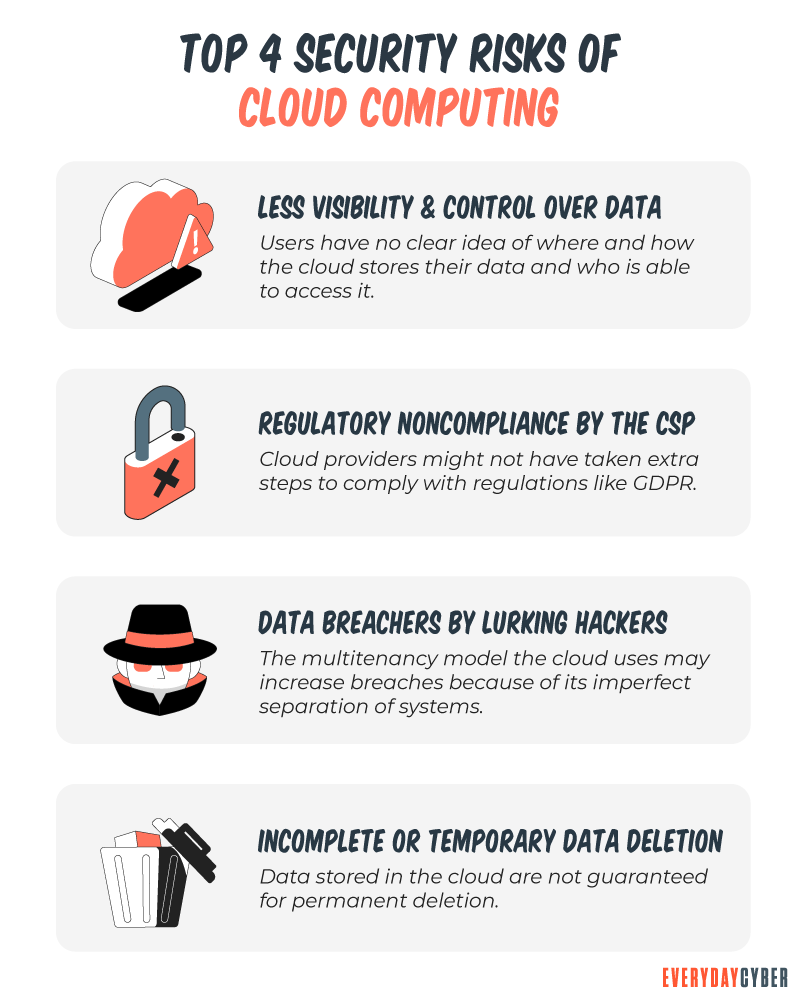
These weaknesses opened vulnerabilities that hackers gladly exploit. Wrong configuration was the leading cause of small business cyber attacks in 2020.
How to deal with this:
Prepare your infrastructure before transferring data to the cloud. Be aware of added vulnerabilities that cloud services may bring. Partner with a trusted cloud service provider.
5. Multi-factor authentication is gaining popularity
This is a positive trend that small businesses are embracing. But then again, threat actors are keeping up with the trends. They have found new ways to hijack some methods of authentication. More specifically, they’re seizing control of authentication through SMS and
SMS has some built-in
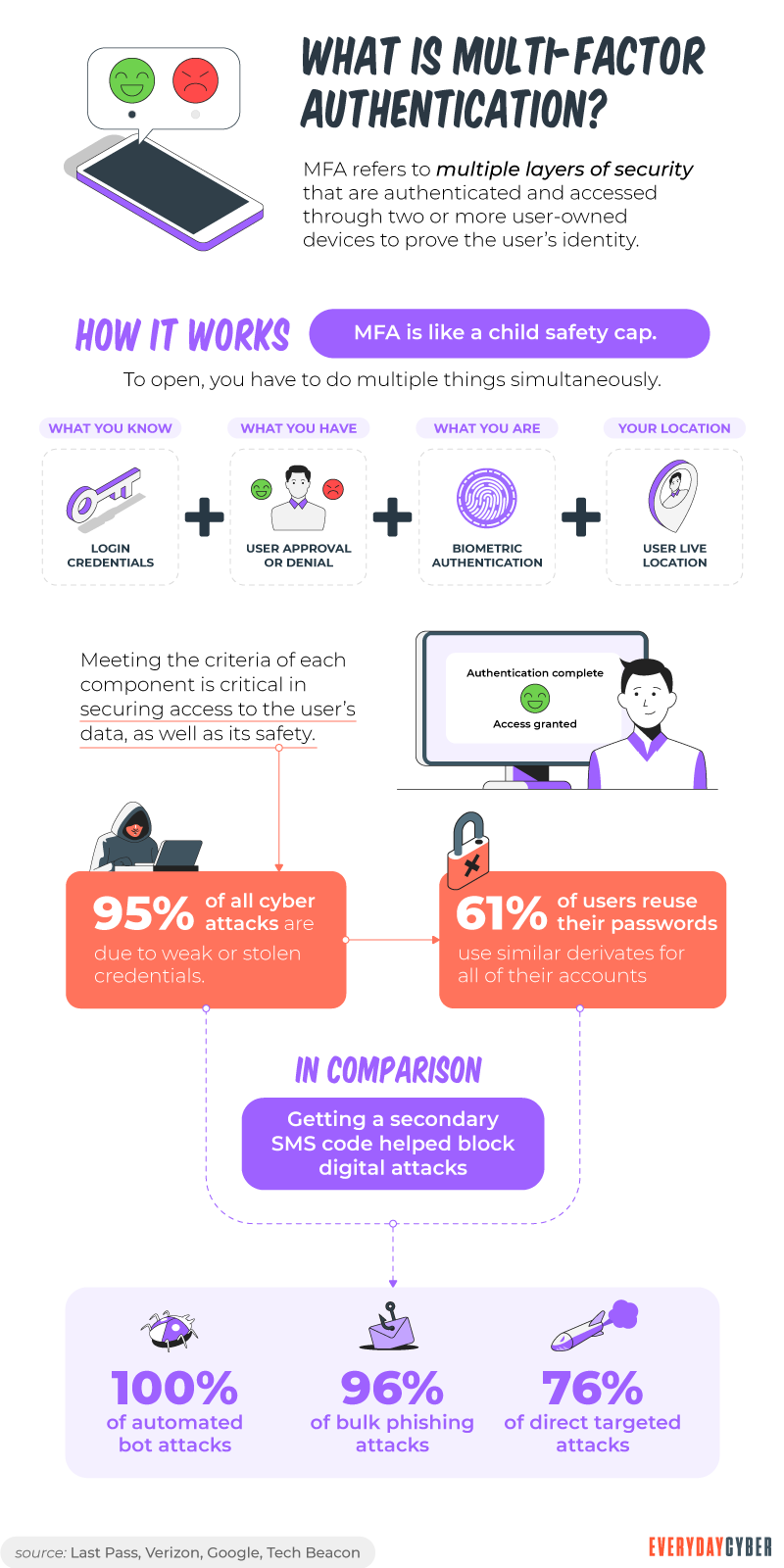
How to deal with this:
Financial institutions must turn to app-based authentication. Consider using Google Authenticator, Microsoft Authenticator, Authy 2-Factor Authentication, and other similar apps.
6. Mobile devices are attractive targets for hackers
Two-thirds of the world’s population use smart
People often carry with them their phones, tablets, and wearables. They use these devices for many of their online transactions. For example, they use their phones or laptops when they bank, shop, or travel.
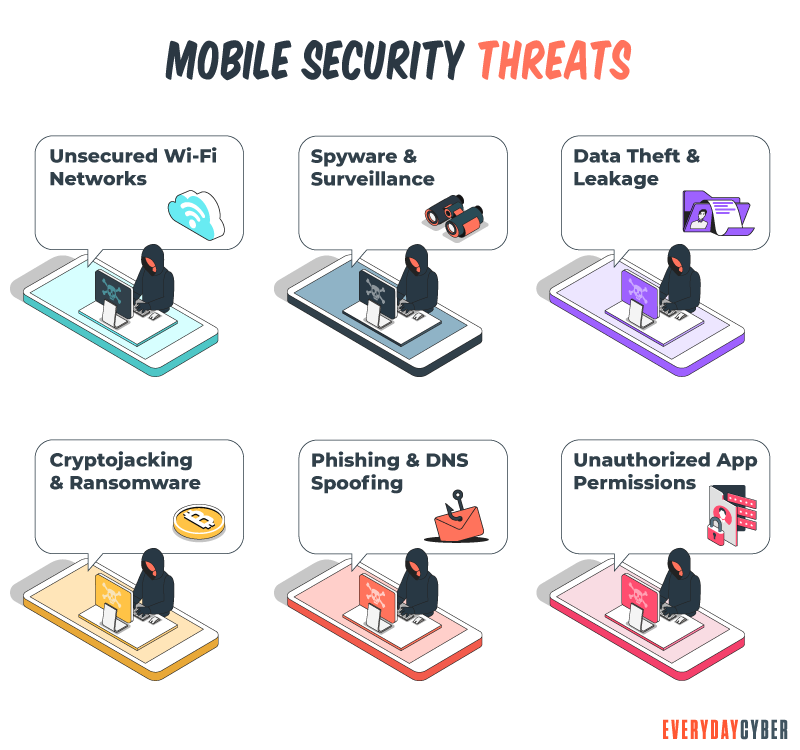
Cyber criminals are happy with the widespread use of
How to deal with this:
There is no single method of protecting different kinds of
7. Phishing remains a very devastating cyber threat to small businesses
And there are no signs it will stop soon. Phishing scams continue to use emails as launching pads for cyber threats. It’s scary because phishing is moving at full speed with more varieties.
Phishing emails often target employees working from remote places. Many employees use unsecured personal gadgets to connect to their company networks. Add to that sophisticated social engineering tactics and you have an almost perfect cyber breach.
Attackers adapt and refine their techniques to their victims’ habits. Social engineering makes it hard to detect the attacks. Phishing victims easily fall for the perceived legitimacy of the phishing emails.
How to deal with this:
Phishers use fake identities to carry out their devious acts. Employees should undergo
8. Insider threats are growing
Insider threats come from actors you never suspect. They are lurking around company cubicles. They’re waiting for an opportunity to attack when employers least expect it, doing their regular tasks to avoid detection.
Insiders may be current employees that misuse company information. They are financially motivated and want to generate extra income. Gartner estimates insiders make up 62% of all malicious players.
Disgruntled current or former employees also contribute to insider threats. They deliberately steal information or sabotage the company. Gartner’s threat statistics show that 29% of this group are motivated by money. About 9% are driven by a vindictive desire to commit sabotage against the company.
Some employees exhibit compliant behavior toward cyber
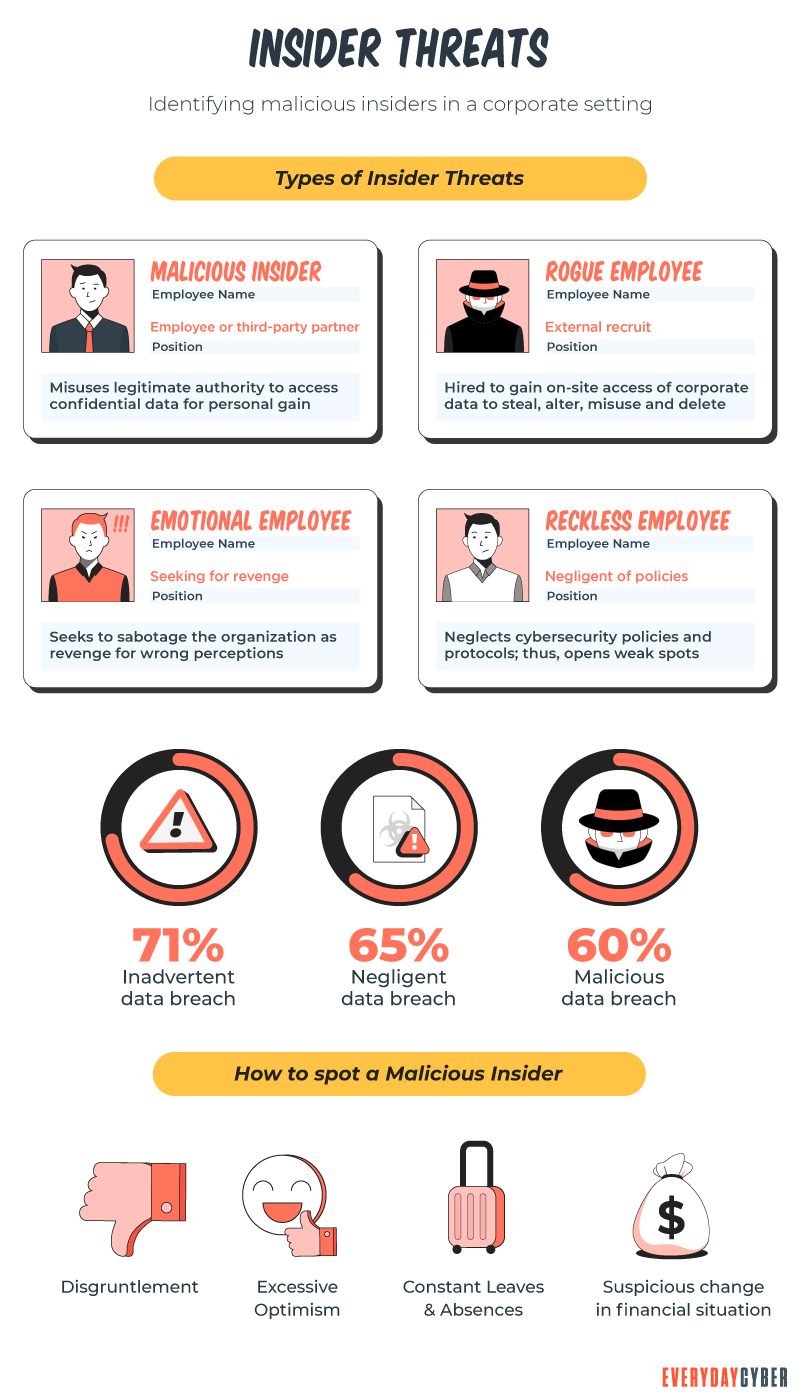
Malicious insiders are more dangerous because they know their way around current
Some company executives are also partly to blame. They don’t take
According to a recent Verizon report, 34% of cyber attacks are caused by employee mistakes. The occurrence of insider attacks is projected to grow in 2021.
How to deal with this:
Insider threats are often triggered by excess access or abuse of access. Companies should develop a perfect balance between granting access and limiting access. Give the right access to the right user when they need it in their job, or no access when they don’t need it to do their job.
9. Data privacy will no longer be a mere component of a security program, but a program in itself
Sensitive data is the single most important target of attackers. Companies are increasingly concerned with merciless data breach attempts. Many are moving toward making data privacy a discipline. The European Union has started its own General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). So far, it’s the toughest privacy and
GDPR was crafted and passed by the EU. But it covers all organizations around the globe that want to collect data related to people in the EU. The regulation imposes fines against violators of its privacy and
How to deal with this:
Data privacy impacts almost every aspect of an organization. A data privacy discipline involves the creation of a data privacy management system. You must have a competent chief

10. Artificial intelligence (AI) is expected to automate threat analysis
The sheer volume of cybersecurity threats is overwhelming to human capabilities. AI is expected to simplify the analysis of tons of cyber
AI can establish threat patterns and malicious cyber behaviors. It uses as much data for as many potential scenarios as possible more quickly than humans. This saves time and money for cyber
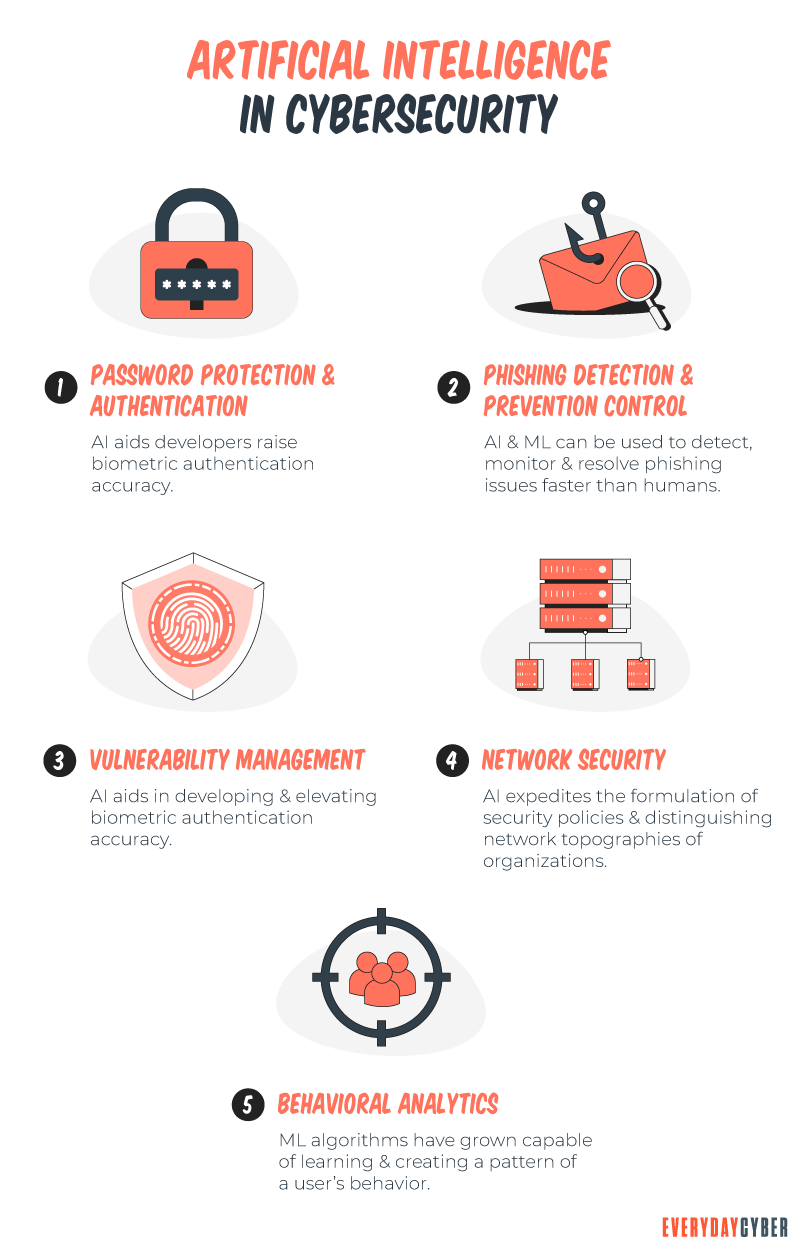
Many businesses have yet to embrace AI. The practical applications of AI are still developing. Companies expect it to grow in sophistication and capabilities. They want something that can beat automated cyber
How to deal with this:
AI is not only for larger businesses. It’s relatively expensive because it’s still in its early stages. It can also benefit smaller businesses whose
By entering your email address you agree to receive emails from EveryDayCyber. We'll respect your privacy and you can unsubscribe at any time.
Our final thoughts
The same is true for cyber criminals. They continue to search for new ways to harm people and organizations. But there’s no stopping digital transformation while cyber
We hope what we shared will help you adopt cybersecurity best practices. These will also help you shape a foolproof cybersecurity strategy.
Being aware of them helps you take the right action to ensure a good future for your small business.
By entering your email address you agree to receive emails from EveryDayCyber. We'll respect your privacy and you can unsubscribe at any time.
Recommended Reading
What is DNS Hijacking?
DNS hijacking is no laughing matter. It is a serious security threat that is consuming the cyber world. The critical role of DNS for network security has made a primary target for facilitating mass data theft.
What is a Hacker?
A hacker is someone who challenges technology to see if it can be compromised. A hacker can black hat or white hat.
7 ways to secure your home office
People working from home perform most of their tasks online. They are now more exposed to cyber attacks than ever before. Cyber criminals see a great opportunity in the massive growth in working from home and the vulnerabilities of home office security.
Element Chat Review: How Secure Is It, Really?
Element is a secure messaging app for safer personal and corporate communication and other group chats.
What is Spear Phishing?
Spear phishing is a targeted cyberattack to steal your information. You should be aware of the dangers of this and how to address them.
The #1 Cyber Threat Small Businesses are Facing
Phishing attacks are the most widespread and most damaging threat to small businesses, accounting for 90% of all cyber security breaches.





